A deep cultural crisis
Sigmund Freud
Freud was born in 1856 in the Austro-Hungarian empire, and died in 1939. For most of his life he was raised in Vienna, then came to the USA where he made a presentation of his theory at Clark University in Massachusetts. He was diagnosed with cancer. Though Jewish, Freud's fame saved him until the Nazi's party burned his books throughout Germany so that he fled to England.
He started to write down his dreams, convinced that they might offer clues to the workings of the unconscious, a notion he borrowed from the romantics
The theme goes like this:
- dreams are : -the fulfilment of a wish
-the disguised fulfilment of a repressed wish
-the disguised fulfilment of a repressed infantile wish
He wrote three essays which dealt with perversions, discussing sexuality in infancy and childhood. In particular he discovered that abnormal events during childhood lead to adult sexual aberrations.
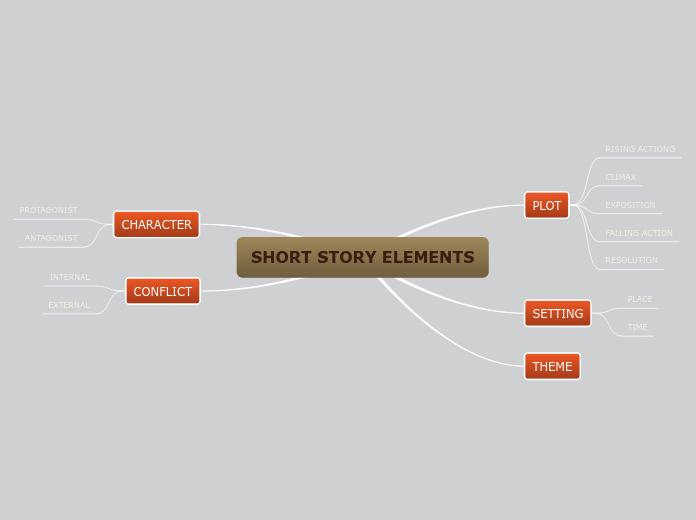
"Oedipus complex": the little boy loves his mother and hates his father, proves that the erotic desire starts in infancy not in puberty
Is identified in three parts:
-"ID": the set of instinctual impulses
-"EGO": the coordinated realistic part
-"SUPEREGO": the critical and moralising role that includes the constraints imposed by society and moral laws
He developed the rules of psychoanalytic therapy, based on largely silent listener who encourages the patient to say whatever comes to mind, no matter how foolish it is
The effects in the family sphere were profound, since the relationship between parents and children were altered
The development of the human psyche is deeply affected by the subconscious. The fact that actions could be related to irrational forces provoked a sense of conflict
Albert Einstein
Space and time are deeply connected and form a four dimensional continuum, which is curved, called "space-time". Mass and energy would wrap space-time; indeed their paths would appear to be bent by a gravitational field.
In 1905 he wrote one of the fundaments of the theory of relativity, in which he pointed out that the laws of science should appear the same to all freely moving observers. In particular they should measure the same speed of light.
Nothing could move faster than light. Indeed as energy is used to accelerate a particle or a spaceship, the object's mass increases making it harder to accelerate anymore. It means that to accelerate a particle to the speed of light is impossible, because it would take an infinite amount of energy.
If the nucleus of a uranium atom fissions split into two nuclei with slightly less total mass, a tremendous amount of energy is released.
Einstein was convinced by scientists to write a letter to president Roosevelt, urging the USA to start a program of nuclear research.
This encouraged the Manhattan project, that led the atom bomb that exploded over Hiroshima in 1945. Einstein wasn't part of this project and was horrified by the explosion.
E=mc^2
For observers moving relative to each other at constant speeds, length and time measurements are different (perhaps drastically different if the speed is
close to the speed of light).
There is not a universal time, but every one had his own personal time. Time is neither linear nor absolute but relative.
If a stationary observer watches a clock moving at the speed of light, he sees it ticking more slowly than an observer travelling with the clock.
He was born in 1879 in Germany and died in 1955 in New Jersey. He was an "average" pupil but from an early age became interested in science and mathematics. When the Nazis came to power, he was forced to leave Germany; he came to America, where changed the composition of university faculties. During the World War I he wrote an antiwar petition, while after the World War II he took part in campaigns for a ban on nuclear weapons.
During the last decades of the 19th century, the system of Victorian values faded.
The dissolution of the empire into a "common wealth of nations" induced a sense of frustration
A cultural crisis and a cynical mood spread after the First World War which filled the conscience with the atrocities of the war
The difference between generations was considered as the main responsible for the waste of lives during the war
The faith in progress and science had led humanity to believe that all the misery would be swept away.
Science and religion didn’t have certainties and nothing seemed to be right
Scientists came up with new views of the universe, as for instance the theory of special relativity