af Ana Cassini 1 år siden
172
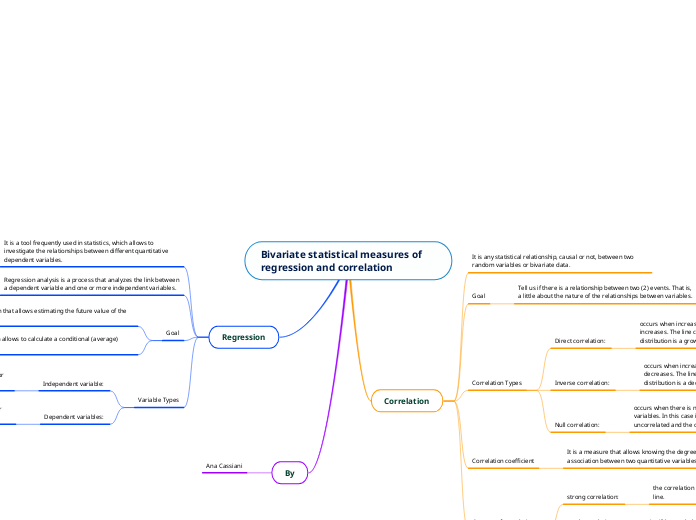
Bivariate statistical measures of regression and correlation
af Ana Cassini 1 år siden
172

Mere som dette
are the attributes on which we want to measure changes or make predictions.
they represent inputs or causes, that is, potential reasons for variation.
here there is no type of pattern or relationship between them.
it will be weak the further apart the points are on the line.
the correlation will be strong the closer the points are to the line.
occurs when there is no dependency of any kind between the variables. In this case it is said that the variables are uncorrelated and the cloud of points has a rounded shape.
occurs when increasing one of the variables, the other decreases. The line corresponding to the cloud of points of the distribution is a decreasing line.
occurs when increasing one of the variables, the other increases. The line corresponding to the cloud of points of the distribution is a growing line.