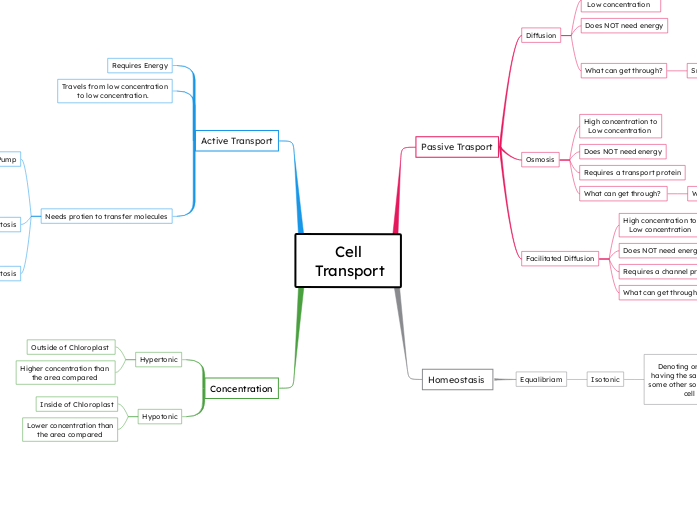
Cell
Transport
Concentration
Hypotonic
Lower concentration than
the area compared
Inside of Chloroplast
Hypertonic
Higher concentration than
the area compared
Outside of Chloroplast
Active Transport
Needs protien to transfer molecules
Exocytosis
A process that occurs when a cell moves large materials from inside the cell to the outside of the cell using small spheres of membrane called vesicles
Endocytosis
The process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle
Pump
Protein= ADT
( Adenosine Tri Phosphate)
Contractile Vacuole
Na+/K+ Pump
Travels from low concentration
to low concentration.
Requires Energy
Homeostasis
Equalibriam
Isotonic
Denoting or relating to a solution having the same osmotic pressure as some other solution, especially one in a cell or a body fluid
Same concentration
Passive Trasport
Facilitated Diffusion
Glucose
Requires a channel protien
Glucose carrier protein
High concentration to
Low concentration
Osmosis
What can get through?
Requires a transport protein
High concentration to
Low concentration
Diffusion
What can get through?
Small and uncharged
Carbon Dioxide
Oxygen
Water
Does NOT need energy
High Concertation to
Low concentration