af Hailey Satar - Aylesbury PS (1425) 2 år siden
123
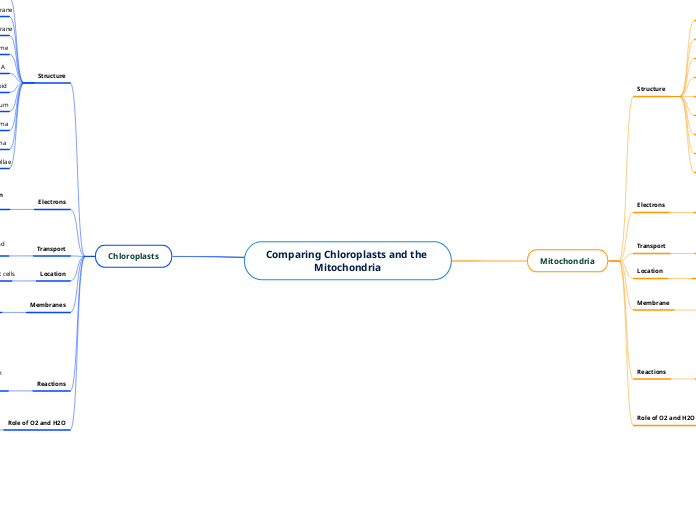
Comparing Chloroplasts and the Mitochondria
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are vital organelles found in eukaryotic cells, each playing crucial roles in energy production. Mitochondria, located in the cytoplasm, are the powerhouses of the cell where cellular respiration occurs.