Cooking Methods
Moist Heat Cooking
What Is Moist Heat Cooking
Techniques that involve cooking with moisture, either directly or indirectly-whether its steam, water, stock, wine or some other liquid.
Types of Moist Cooking
Poaching
Poaching is a low-temperature, moist-heat cooking method from 140-190°F/60-88°C suitable for delicate, lean proteins, like fish, shellfish, poultry breasts, and beef or pork tenderloin.
Simmering
Simmering is a cooking method that brings the liquid of a dish to just below the boiling point over lower heat. This method uses moderate heat to soften foods slowly over time, before gradually adding seasonings and other ingredients to the dish. EX. stews
Stewing
Stewing refers to a dish of meat, vegetables or fruits cooked slowly in liquid using low heat in a closed dish or pan. This method is considered a moist heat form of cooking when describing fruit and vegetable cookery (stewed tomatoes, stewed prunes).
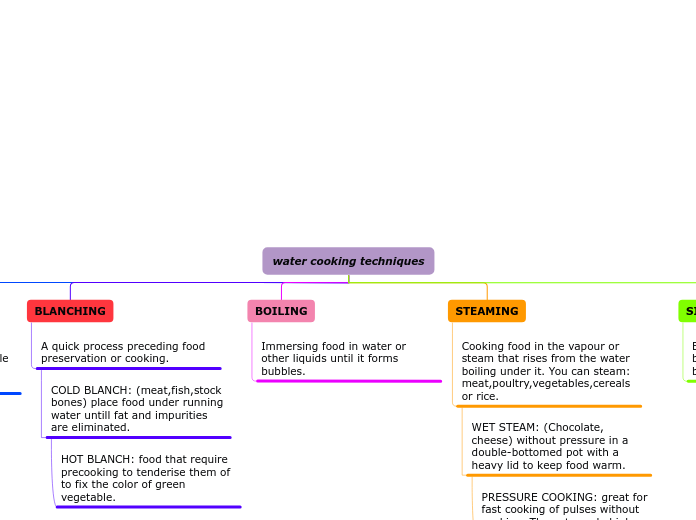
Steaming
Steaming is a method of cooking that requires moist heat. The heat is created by boiling water which vaporizes into steam. The steam brings heat to the food and cooks it. EX. Dim sum
Boiling
Boiling is a cooking method where a liquid is heated to the temperature where it becomes a vapour. This occurs at a temperature of 100C or 212F. EX. Pasta
Blanching
Blanching is scalding vegetables in boiling water or steam for a short time. EX. Green beans
Braising
Braising uses dry and moist-heat cooking methods. First, less tender cuts of meats are commonly browned in fat or oil at high temperatures. Then, vegetables and seasonings are generally added; normally with a liquid or sauce of some complementary. EX. Red braised pork belly
Dry Heat Cooking
What Is Dry Cooking
Cooking technique where the heat is transferred to the food item without using any moisture.
Types of Dry Cooking Methods
Dehydrating
Dehydrating is a process whereby all
moisture is removed from a food in order to preserve it as a shelf stable food. EX. A grape becomes a raisin
Smoking
Smoking is a process where meats are cooked, flavoured and preserved using very low heat source and the creation of smoke from a variety of burning woods. EX. Salmon, herring, and oysters
Flambéing
Flambéing is where alcohol is added to a hot pan in which foods are being cooked and is lit on fire. EX. Bombe Alaska
Roasting
Roasting is a slow-cooking process, using indirect, diffused heat to cook its ingredients. It is a dry-heat cooking method where hot air surrounds the food and cooks it evenly on all sides. EX. Garlic Roasted Potatoes
Grilling
Grilling in the kitchen provides a quick cooking method that imparts flavour to a food product by allowing the browning process to happen quickly and effectively. Grilling uses a bottom heat source (gas, propane, coal or wood) and a metal rack or grate. EX. Steaks and chops are suitable for grilling as they
require high heat for a short period of time.
Broiling
Broiling exposes food directly to a heat source usually from above by either a stove element (such as the broiling option on an electric stove) a gas flame (using a broiling instrument such as a salamander or a torch). The purpose of broiling is to retain the juiciness of the food you are cooking while adding additional flavour. EX. strip steaks
Deep Frying
Large amounts of oil or fat are used in cooking the food. The oil or fat is usually put into a deep pan or well and is heated between 350-400 F.
Food is then submerged in the oil until it is cooked through. EX. French fries
Sautéing
Sautéing is a form of dry-heat cooking that uses a very hot pan and a small amount of fat to quickly cook food while browning the surface. EX. Stir fried beef
Baking
Baking refers to a uncovered product that is cooked by the heated air produced in a closed oven between 300-500 degrees Fahrenheit. EX. Breads, cakes and pastries.