TREATMENT
co-morbidity considerations
weight gain concerns
AVOID INSTI+TAF
Psychiatric illiness
AVOID rilpivirine
AVOID efavirenz
Hyperlipidemia
use TDF
High cardiac risk
AVOID abacavir & PI
Hep B
use TENOFOVIR
AVOID abacavir
treatment naiive
start ASAP
use backup method for the 1st
6 months or until viral load is undetectable
2 drug regimen
dolutegravir (INSTI) + lamivudine (NRTI)
***ONLY USE IF VIRAL LOAD
< 500,000, NO HBV AND GENOTYPIC RESULTS AVAILABLE
3 drug regimen- preferred
NRTI + NRTI + INSTI (or NNRTI*)
*generally dont use NNRTI if viral load > 100,000 copies and/or CD4<200
TAF/TDF w/ emtricitibine/lamivudine + doultegravir
abacavir/lamivudine +
dolutegravir
TAF/emetricitabine +
bictegravir
Natural PATHO
HIV LIFE CYCLE
lyses
maturation
budding
assembly
translation
transcription (mRNA-->DNA)
DNA migrates to nucleus to be INTEGRATED into host DNA
reverse transcription (RNA ---> DNA)
uncoating
fusion
secondary binding of HIV to co-receptors CCR5 or CXCR4
HIV binds to CD4 receptors
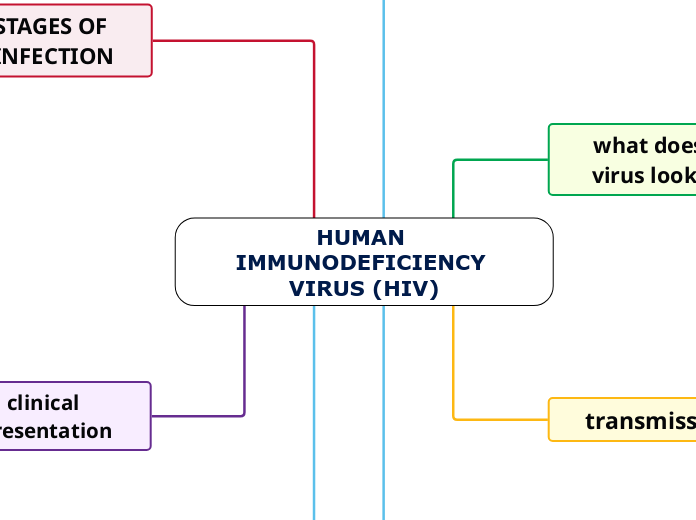
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV)
TESTS TAKE ABOUT 2-3 WEEKS BEFORE THEY CAN DETECT A NEW HIV INFECTION
clinical presentation
often presents with OI or cancer
asx
sx
WEIGHT LOSS
NIGHT SWEATS
if you see these sx think of either
B-cell lymphoma, TB, or HIV
may be asx
STAGES OF INFECTION
no tx--> 3 year life expectancy
prone to OI
CD4 < 200
preventable w/ tx
chronic
U=U
undetectable viral load = untransmittable HIV
HIV reservoirs
asx/clinical latency
acute
high viral load
flu-like sx or symptomatic
GOALS
want a high CD4 count and a low viral load
CD4 count
> 500 copies/mL
viral load
undetectable
< 200 copies/mL
transmission
exchange of bodily fluids
highest risk sex act = receptive anal
lowest risk sex act = insertive anal/vaginal
what does the virus look like?
retrovirus
RNA
single stranded
enveloped
how to distinguish HIV vs. AIDS
AIDS
indicator conditions
cancer
opportunistic infection
(OI)
examples
MAC
CMV
Encephalopathy
Fungal infections
CD4 COUNT < 200
immune system cant keep
infection in check
severe infection
HIV
acute and chronic phases
infection