INFOXICACIÓN VS CAPACIDAD DE FILTRADO: COMPETENCIA DIGITAL
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
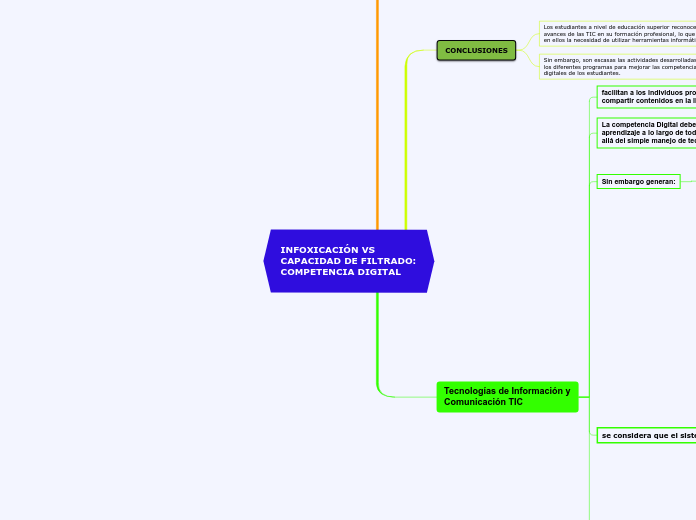
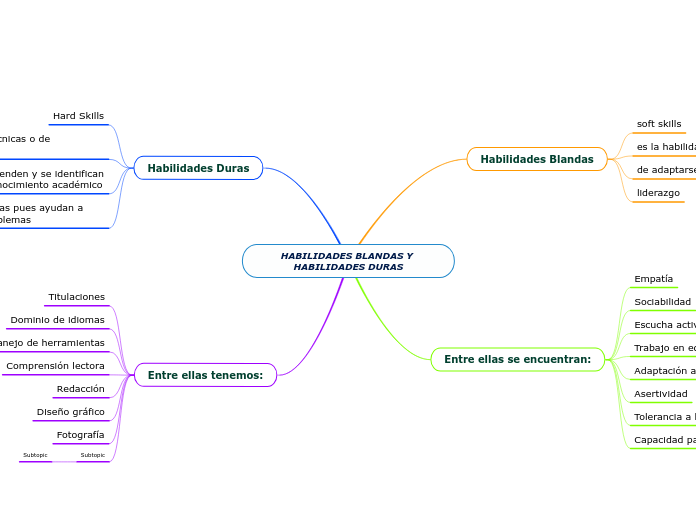
Tecnologías de Información y Comunicación TIC
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
la desconexió: favorece un trabajo mental más reflexivo, crítico, productivo y creativo, y ayuda a la educación emocional
Reciprocal pronouns are used for actions or feelings that are reciprocated. The reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Each other, one another
se considera que el sistema educativo debe
educar a los jóvenes para que no desarrollen comportamientos adictivos al uso de las TIC
A reflexive pronoun ends with ...self or ...selves and refers to another noun or pronoun in the sentence (usually the subject of the sentence). The reflexive pronouns are myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Itself, Himself
desarrollar pensamiento flexible: capacidad de adaptación que tienen los individuos ante los cambios constantes
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
This, These
adquirir habilidades que permitan trabajar de manera colaborativa, capacidad de concentración y desconexión
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
His, Your
favorezcan la solución de problemas reales de forma creativa e innovadora
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
She is the prettiest princess.
emplear de forma segura y crítica las TIC, de tal manera que puedan ser utilizadas en la vida social y profesional, en actividades relacionadas con el trabajo, ocio y comunicación
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
He is taller than she is.
formen a los ciudadanos en competencias digitales
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
Candlestick
acceder con éxito a la información y tener las capacidades cognitivas para transformarla en conocimiento
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Family, Class
Enseñar a buscar, y a discriminar lo que vale la pena (es relevante) de lo que no
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Cats, Rain
cambiar y aprovechar la información dispuesta en la Web para fomentar las capacidades de los individuos de manejarla
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Mary, Paris
Sin embargo generan:
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
infoxicación o infosaturación: el exceso de información que genera confusión en los usuarios de las TIC, incrementan la confusion y la ignorancia.
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
You have been practicing hard.
La competencia Digital debe ser un proceso de aprendizaje a lo largo de toda la vida, que va más allá del simple manejo de tecnología
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
He, They
facilitan a los individuos producir, acceder y compartir contenidos en la llamada era digital.
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
They have it.
CONCLUSIONES
Sin embargo, son escasas las actividades desarrolladas desde los diferentes programas para mejorar las competencias digitales de los estudiantes.
Los estudiantes a nivel de educación superior reconocen los avances de las TIC en su formación profesional, lo que genera en ellos la necesidad de utilizar herramientas informáticas
Resultado
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
A partir de los ejercicios de búsqueda de información que deben realizar los estudiantes
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
se pudo establecer que no han sido formados para desarrollar competencias digitales utilizando las TIC
Indefinite articles are the words 'a' and 'an.' Each of these articles is used to refer to a noun, but the noun being referred to is not a specific person, place, object, or idea. It can be any noun from a group of nouns.
A car in the parking lot.
Aunque los estudiantes reportaban la fuente, estas eran de bajo valor académico y en muchos casos no presentaban el autor o año de publicación
It refers directly to a specific noun or groups of nouns.
The breakfast on my plate.
se limitaban a copiar las definiciones del tema tal como la presentaban en internet sin realizar ejercicios rigurosos de lectura y escritura
Unlike demonstrative pronouns, which point out specific items, indefinite pronouns are used for non-specific things. This is the largest group of pronouns. All, some, any, several, anyone, nobody, each, both, few, either, none, one, and no one are the most common.
None, Several
Los estudiantes no evaluaban las fuentes y se les dificultaba encontrar información pertinente y fiable
Relative pronouns are used to add more information to a sentence. Which, that, who (including whom and whose), and where are all relative pronouns.
Create sentences
Which, Where