af Ayesha Rahman 7 måneder siden
137
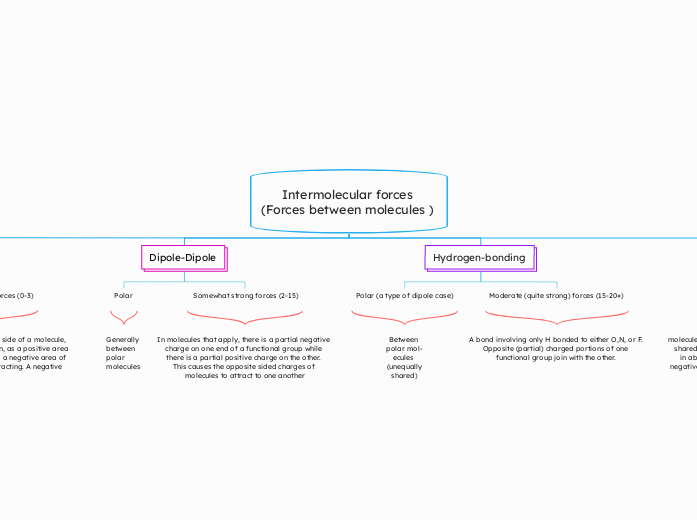
Intermolecular forces (Forces between molecules )
Molecules interact through various intermolecular forces, which are essential to understanding their behavior and properties. When an electron is on one side of a molecule, it creates a momentary attraction due to the exposure of a positive area to a negative area, leading to an attraction between molecules.