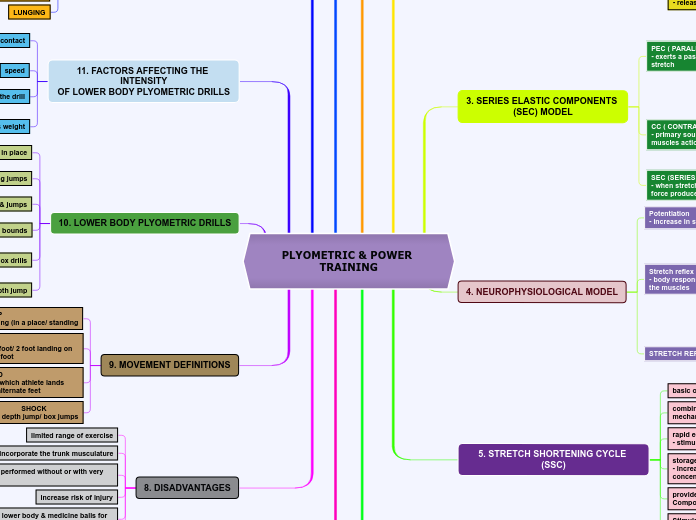
PLYOMETRIC & POWER TRAINING
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
7. ADVANTAGES
When a preposition consists of one word it is called single or simple preposition.
no deceleration phase
promoting the development of muscular power
performed exercise at higher velocities vs. traditional weight training.
adopted in most sporting actions
performed in a more explosive way than speed
training and traditional weight
Requires athlete to rapidly develop force
production of high forces and acceleration throughout full ROM
8. DISADVANTAGES
A preposition is one of the most exciting parts of grammar. A preposition is used to describe the location of something in relation to something else.
time constraints with exercise progression
use body mass for lower body & medicine balls for upper body
increase risk of injury
exercise generally performed without or with very limited feedback
difficult to incorporate the trunk musculature
limited range of exercise
9. MOVEMENT DEFINITIONS
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
SHOCK
- In depth jump/ box jumps
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
down-toners
Fairly, Rather
intensifiers
Extremely, Very
BOUND
- series of movements in which athlete lands successively on alternate feet
Just, Afterward, Soon, Currently
HOP
- Starts & concludes with 1 foot/ 2 foot landing on the same foot
Always, usually, Never
JUMP
- concludes with 2 foot landing (in a place/ standing
Carefully, Slowly
10. LOWER BODY PLYOMETRIC DRILLS
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
depth jump
use gravity for athlete weight to increase exercise intensity
box drills
increase the intensity of multiple hops and jumps by using box
bounds
exaggerated movements with greater horizontal speed
multiple hops & jumps
Involve repeated movements
standing jumps
emphasize either horizontal or vertical components
jumps in place
jump and land in the same spot
11. FACTORS AFFECTING THE INTENSITY
OF LOWER BODY PLYOMETRIC DRILLS
participant's weight
the greater the athlete weight, the more stress is placed on the msucles
height of the drill
the higher body's center of gravity, the greater force on the landing
speed
greater speed increase the intensity of the drill
points of contact
the grand reaction force during single leg lower body, plyometric drills places more stress on muscle, tissue and joints
12. PLYOMETRIC WARM-UP DRILLS
LUNGING
FOOTWORK
SKIPPING
JOGING
MARCHING
13. IMPLEMENTING A PLYOMETRIC PROGRAM
properly progress the program
teach the athlete proper technique
determine program design variables
establish sport specific goals
equipment & facilities provide safe environment
evaluate the athletes
6. PHASES OF SSC
III. Concentric phase (shortening of agonist muscle)
- elastic energy release from SEC
- alpha motor neuron stimulate agonist muscle group
II. Amortization phase ( pause between phase I & II)
- afferent nerve synapse alpha neuron motor
- alpha motor neuron transmit signal to agonist muscle group
I. Eccentric phase ( stretch of agonist muscle)
- elastic store in SEC ' muscle spindle stimulated'
5. STRETCH SHORTENING CYCLE (SSC)
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Stimulation of stretch reflex to facilitate a maximal increase in muscle over a minimal time
provide energy storage of Series Elastic Components (SEC)
storage of elastic energy
- increase the force produced during the next concentric action
rapid eccentric muscle action
- stimulates stretch reflex
combination of mechanical & neurophysiological mechanism
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
basic of plyometric eercise
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
This stew is savory and delicious.
4. NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL MODEL
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
STRETCH REFLEX
An article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Technically, an article is an adjective, which is any word that modifies a noun.
muscle spindle > muscle stretch stimulated > travel to spinal cord via nerve fiber > synapsing with alpha motor neuron in spinal cord > travel to agonist extrafusal fibers > reflexive muscle action
It refers directly to a specific noun or groups of nouns.
The breakfast on my plate.
Stretch reflex
- body response to external stimulus that stretches the muscles
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
Plyometric
(reflexive muscle action when muscle spindle
stimulated by rapid stretch)
quick stretch
(muscles increase reflexively)
muscle spindle
Potentiation
- increase in strength impulse
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
change in force-velocity of muscle
contraction caused by stretch reflex
3. SERIES ELASTIC COMPONENTS
(SEC) MODEL
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
SEC (SERIES ELASTIC COMPONENT)
- when stretched, store energy elastic increased force produced.
CC ( CONTRACTILE COMPONENT)
- primary source of muscle force during concentric
muscles action
cross-bridges
myosin
actin
PEC ( PARALLEL ELASTIC COMPONENT)
- exerts a passive force with unstimulated muscle stretch
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
sarcolemma
endomysium
perimysium
epimysium
2. MECHANICAL MODEL OF PLYOMETRIC EXERCISE
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
movement immediately followed by
concentric muscle action, stored elastic energy (EE)
- released to increase the total force production.
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Cats, Rain
elastic energy in the musculotendinous
- increase with rapid stretch & store
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Create sentences
Mary, Paris
1. DEFINITION
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
increase the power of subsequent movements by using both the natural elastic components of muscle & tendon and the stretch reflex.
Acceleration & deceleration to create quick, powerful movement through pre-stretch/ countermovement involving the Stretch Shortening Cycle (SSC)
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
to increase power of subsequent movement
using both natural elastic components of
- muscle
- tendon
- stretch reflex