af Yadwinder Singh 3 år siden
297
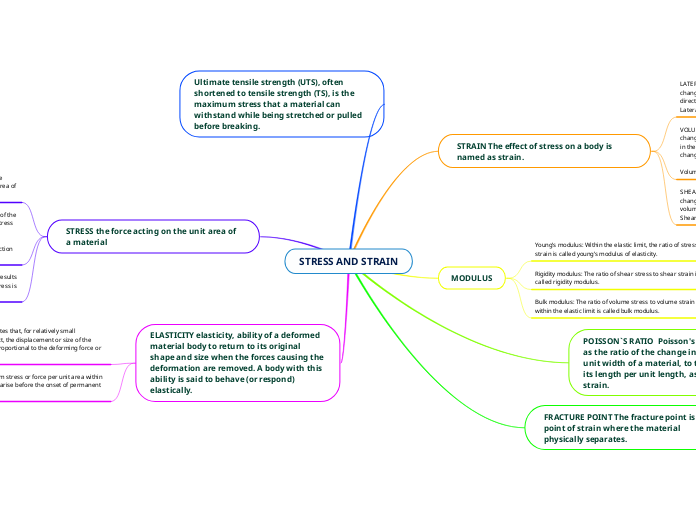
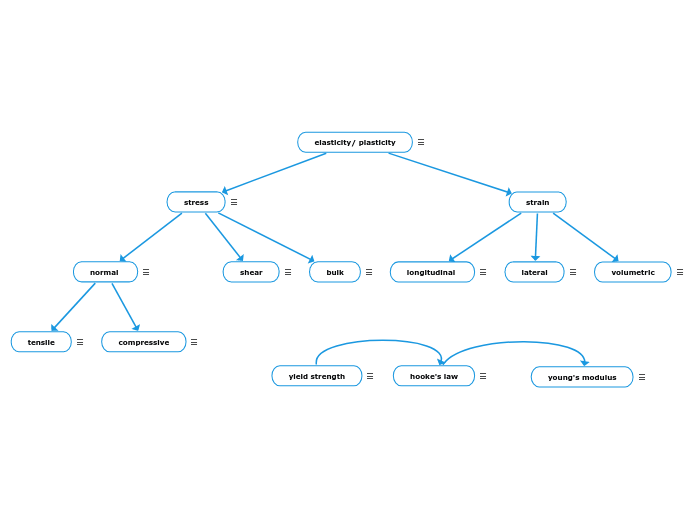
STRESS AND STRAIN
The ability of a material to return to its original shape and size after deformation is known as elasticity. This behavior is governed by Hooke’s Law, which states that small deformations are proportional to the applied force.