af Vanessa Franco 7 år siden
239
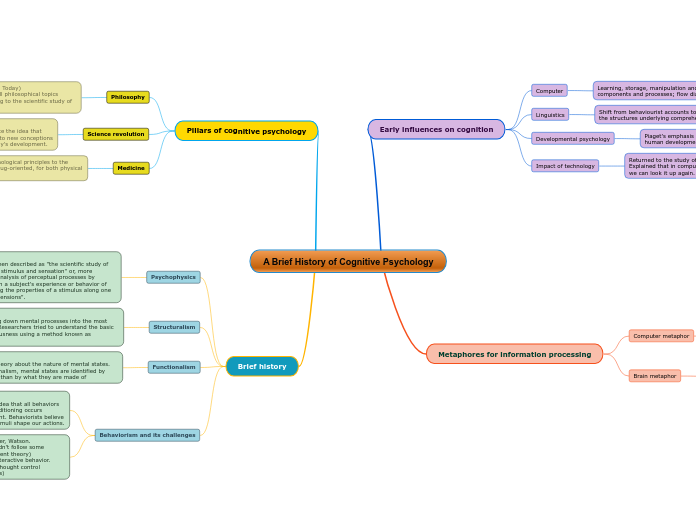
The Inseparable Bodybrain Partnership- Emotions & Movement
The integration of movement and emotion plays a critical role in learning and cognitive performance. The brain's various systems, including the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, and thalamus, are deeply involved in processing emotions and forming memories.