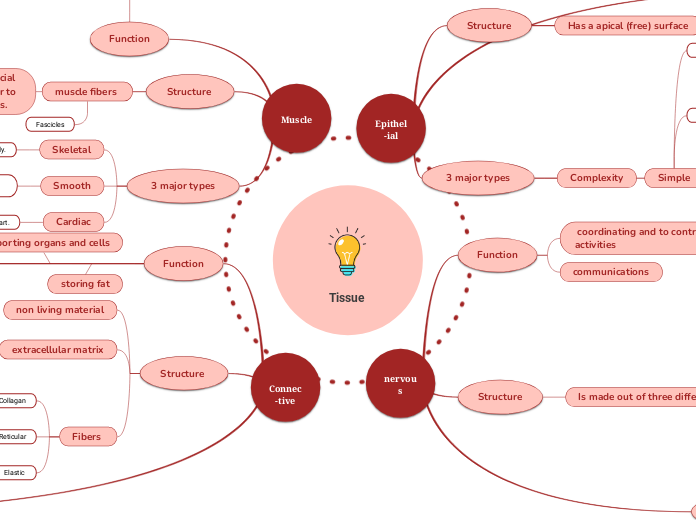
Muscle
Cardiac
The thick middle layer of the heart.
Smooth
Thick and thin filaments that are not arranged into sarcomeres giving it a non-striated pattern.
Skeletal
Providing structural framework and movement to the body.
Composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts.
muscle fibers
Fascicles
provides movement for the body parts.
Connec-tive
4 major types
Fat
Provides insulation and fuel storage.
Connective tissue Proper
dense connective tissue
Stabilize surrounding structures and maintain the structural framework in the body.
loose connective tissue
A cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers.
cartilage
A strong, flexible connective tissue that protects your joints and bones.
Bone
Blood
Structure
Elastic
Provides elasticity and resilience to the tissues.
Reticular
Provide stroma to sustain the lymphoid organs
Collagan
Strongest most abundant fiber
extracellular matrix
Fibers
Ground substance
non living material
repairing damaged tissues
storing fat
defending against pathogens
transporting nutrients and wastes
Supporting organs and cells
nervous
Motor neurons
Transmit impulses from the spinal cord to skeletal and smooth muscles, and so directly control all of our muscle movements.
Sensory neurons
Carries impulses from the receptor to the CNS.
Interneurons
They connect spinal motor and sensory neurons.
Is made out of three different cells
glial cells
Provide support for an essential nervous system function.
neurons
The cells considered to be the basis of nervous tissue.
One axon
The cell body
Transmit information between neurons and away from muscles and glands.
Dendrites
Extensions, or processes, of the cytoplasm that carry impulses to the cell body.
Function
communications
coordinating and to control many body activities
Epithel-ial
3 major types
stratified
More than one layer
Simple
3 shapes
Columnar
more tall than wide
Its found in the lining of the intestine, stomach, and colon.
Cuboidal
cube shaped
Its found in the pancreas, and glands.
Squomous
thin and fat
Its found in the skin.
One layer
Complexity
Structure
made up of epithelial cells
Has a basement membrane
Cells reproduce (quickly)
Has a apical (free) surface
Function
Filtration
Coverage
Secretion of hormones and excretion
Absorption of nutrients
protection of underlining structures
Tissue