Folic acid deficiency anemia
Very similar to Vit B12 deficiency
NO neuro s/s
Malnutrition
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Neuro changes
Ataxia
Paresthesia
Demylination
Megaloblastic
Large RBC
Excess cytoplasmic growth
Short life span
Flimsy membranes
Immature nuclei
Oval
Malabsorption
Long term PPI
Gastric bypass
Gastrectomy
Metformin
Mainly absorbed in the gut
Deficiency
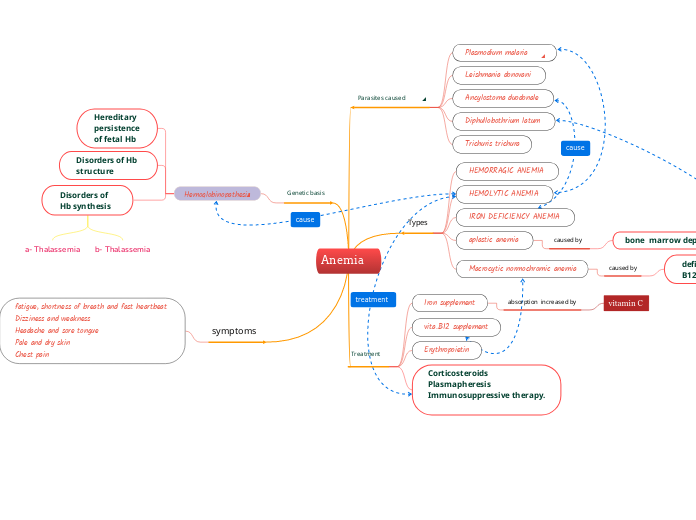
Pernicious anemia
Atrophic gastritis
Failure to absorb B12
Essential for DNA synthesis
Normal RBC maturation
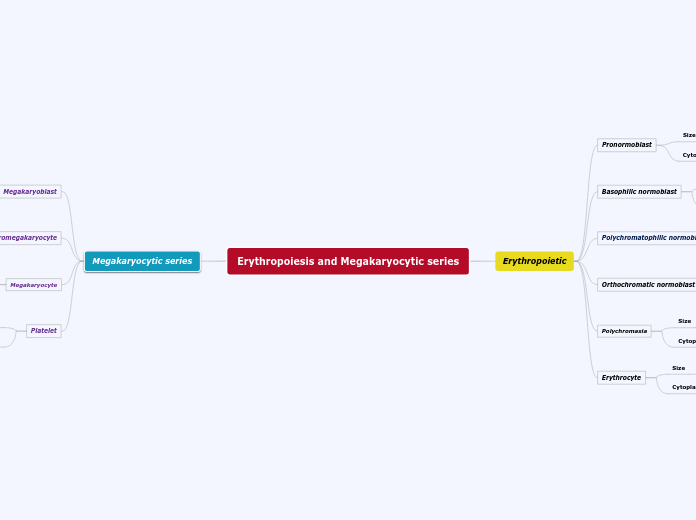
Pluripotent stem cells
Erythroblasts
Reticulocyte
Released into blood stream to mature
Mature RBC = erythrocyte
Red blood cells
Chronic disease anemia
Autoimmune
T-cell activation
Suppress erythropoietin
Osteomylitis
AIDS
CKD
Dyfunctional kidneys
Decreased erythropoietin
Aplastic anemia
Increased bleeding
Gums
GI tract
Vagina
Nose
Decreased platelet level
Dysfunction bone marrow
Can't replace RBC that have been destroyed
Radiation, chemicals and toxins
Hepatitis, AIDs,
Chloramphenicol
Benzene
Chemo
Hematopoiesis
Epithelial atrophy
Brittle hair and nails
Spoon shaped finger deformity
waxy pallor
Iron is reused to form new RBC
Decreased iron = decreased O2 capacity
Increased demand
Children have increased demand due to growth
Cows milk has low absorbable iron
Maternal deficiency
Loss of iron
Bleeding
Menstruation
Pregnant women have increased iron needs
GI
Dietary deficiency
Mostly derived from meat
Vegetarians and deprived populations
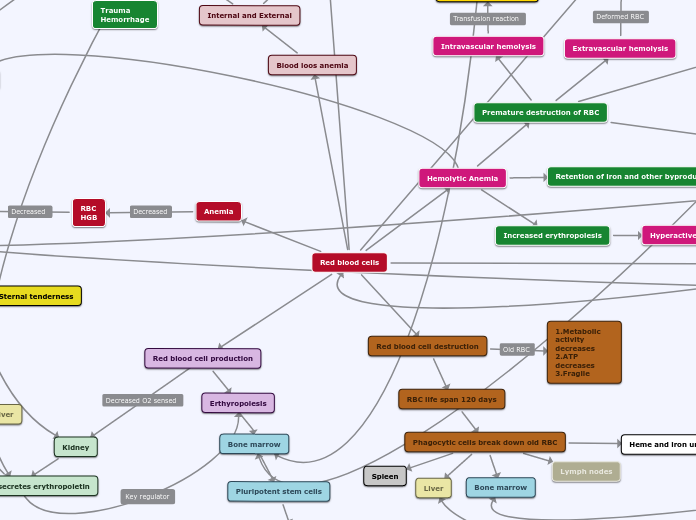
Hemolytic Anemia
Increased erythropoiesis
Hyperactive bone marrow
Increased reticulocytes
Retention of iron and other byproducts
Premature destruction of RBC
Extrinsic
Drugs, toxins, antibodies
Intrinsic
Defective membrane
Sickle cell
"Sickled" shaped cells
Pain
Spleenic injury
Respiratory dysfunction
vasoocclusion
Abnormal HGB
Extravascular hemolysis
Intravascular hemolysis
Hemoglobinemia/uria
Blood loos anemia
Internal and External
Chronic blood loss
Iron deficiency anemia
GI bleed
Menstruation
Iron stores depleted
External leads to iron loss
Trauma
Hemorrhage
Problematic for restoration of RBC
Anemia
RBC
HGB
O2 carrying capacity
S/S
Bone pain
Sternal tenderness
Petechiae & Purpura
Jaundice
Pallor
Conjunctiva
Mucous membrane
Nail beds
Tachycardia
Ventricular hypertropy
CHF
Palpitations
HA
Vision problems
Confusion
Faint
Fatigue
Angina
Dyspnea
Weakness
Red blood cell destruction
1.Metabolic activity decreases
2.ATP decreases
3.Fragile
RBC life span 120 days
Phagocytic cells break down old RBC
Heme and iron units are saved to be reused
Binds to apoferrtin
Converted to transferrin
Taken back to bone marrow to be recycled and reused
Bilirubin
Removed by the liver in the form of bile
Lymph nodes
Bone marrow
Liver
Spleen
Red blood cell production
Erthyropoiesis
Kidney
Produces and secretes erythropoietin
Small portion produced in the liver