two sources
https://bigthink.com/surprising-science/three-groups-who-believe-fake-news
https://coinform.eu/why-do-people-believe-in-fake-news-and-share-it-on-social-media/
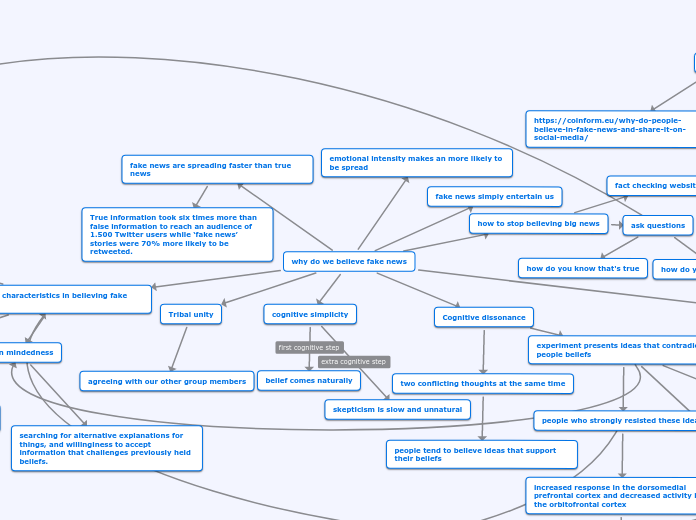
why do we believe fake news
two key characteristics in believing fake news
low in three kinds of people
religious fundamentalists, people prone to delusional thinking, and people prone to dogmatism
analytical thinking
tendency to analyze cause and effect, to consider things logically
open mindedness
searching for alternative explanations for things, and willinginess to accept information that challenges previously held beliefs.
emotional intensity makes an more likely to be spread
fake news simply entertain us
fake news are spreading faster than true news
True information took six times more than false information to reach an audience of 1.500 Twitter users while ‘fake news’ stories were 70% more likely to be retweeted.
how to stop believing big news
fact checking websites
ask questions
how do you know that's true
Tribal unity
agreeing with our other group members
Backfire Effect
believe more on their beliefs because of overwhelming evidence against them
Cognitive dissonance
experiment presents ideas that contradicts people beliefs
belief change is more common in non political beliefs
people who changed their minds
less BOLD signal in the insula and the amygdala
people who strongly resisted these ideas
increased response in the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex and decreased activity in the orbitofrontal cortex
shows how emotions affects our reasoning
two conflicting thoughts at the same time
people tend to believe ideas that support their beliefs
cognitive simplicity
skepticism is slow and unnatural
belief comes naturally