von Moira MS Vor 4 Jahren
296
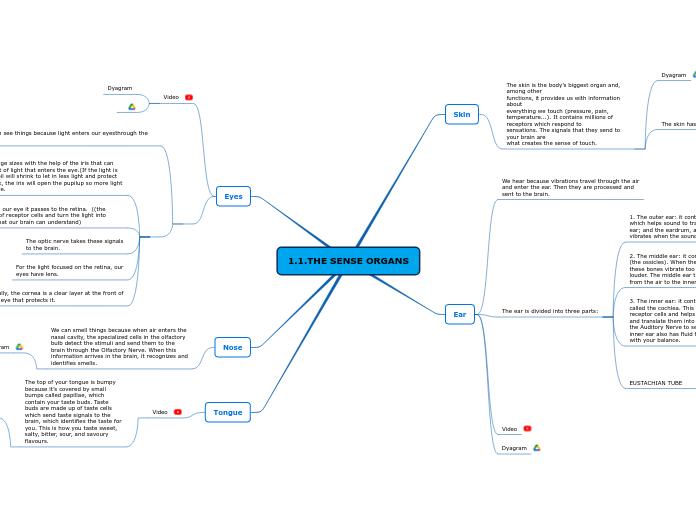
1.1.THE SENSE ORGANS
von Moira MS Vor 4 Jahren
296

Mehr dazu
'Six Thinking Hats' can help you to look at problems from different perspectives, but one at a time, to avoid confusion from too many angles crowding your thinking.
dyagram
This tube runs between the ear and the throat and it keeps the same pressure on both sides of the eardrum. Have you ever had trouble hearing on an airplane? Try yawning or chewing gum and pop! Your eustachian tube will open and you'll be able to hear normally again.
3. Fat layer: it is the inner layer and keeps us warm.
2. Dermis: it is the middle layer, containing sweat glands.
1. Epidermis: it is the outer layer, and it contains specialized cells that receive information from the outside.