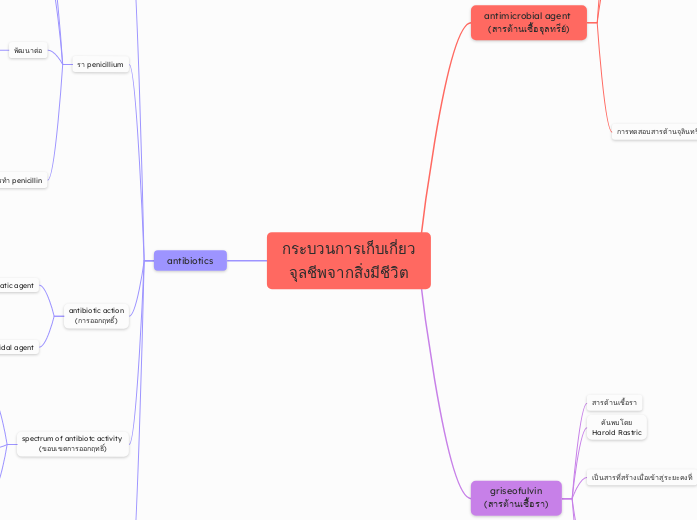
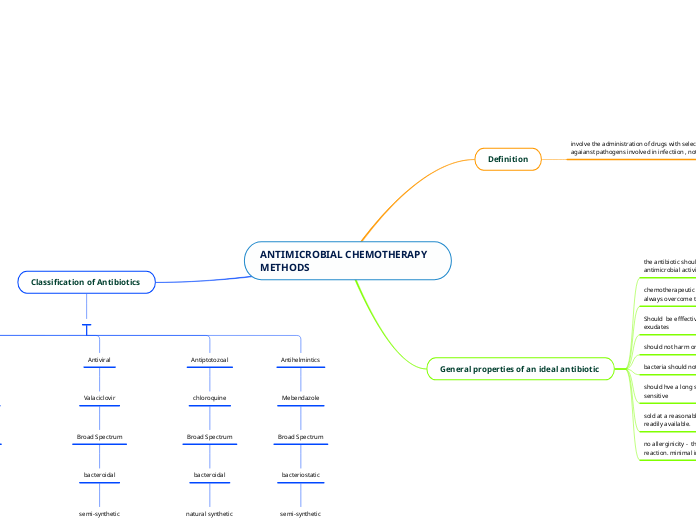
ANTIBIOTICS
CLINICAL USE OF EACH ANTIBIOTICS
Erythromycin
Unidentified respiratory infections
Legionella pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
S. pneumoniae
Staphylococcal infections
penicillin allergic patients
-Isoniazid
-Rifampin
-Ethambutol
-Pyrazinamide
Tuberculosis Agents
Quinolone
Osteomyelitis
Cholera
Shigellosis
Traveller's diarrhoea
Typhoid
Prostatitis
Aminoglycoside
-Streptomycin
-Amikacin
-Gentamycin
-Neomycin
-Netilmicin
Hospital acquired infections
Septicaemia in burn cases
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections
Staphylococcus aureus infections
Chloramphenicol
Topical antimicrobial agent
Anaerobic infection
Rickettsial disease
Pneumococcal &
meningococcal meningitis
in beta-lactam sensetive persons
Trimethoprim
Pneumocystis
pneumonia
Gastrointestinal
infections
RTI
UTI
Tetracyclines
Community-acquired MRSA
S. aureus
Vancomycin resistant enterococcus
Mycoplasma
Rickettsia
Chlamydia
Gram positive & negative bacteria, anaerobes
Fusidic Acid
Staphylococcal infections
in combination
with other antibiotics
Clindamycin
Anaerobic gram negative bacilli
Prevention of infective
endocarditis in patients
allergic to penicillin
Glycopeptides
Vancomycin
teicoplanin
Clostridium difficile
antibiotic associated collitis
Ampicillin resistant enterococcus
endocarditis
MRSA
Carbapenems
Empiric therapy
meningitis
septicaemia
Intra-abdominal sepsis
Broad spectrum
Cephalosporin resistant bacteria
Anaerobic bacteria
Gram negative cocci and rods
Gram positive cocci and rods
Cephalosporin
5th Gen.
Ceftaroline
Gram negative rods
Gram positive cocci (inc MRSA)
4th Gen.
Cefepime
similar to 3rd Gen.
3rd Gen.
ceftriaxone,
cefoxitin
ceftazidime
Gram negative rod
Gram negative cocci
Gram positive cocci
2nd Gen.
Cefaclor
cefuroxime, cefoxitin
Klebsiella & Haemophilus influenzae
mixed aerobic & anaerobic infections anaerobic
1st Gen.
Cephalexin
Respiratory tract infections
UTIs
Gram positive cocci except enterococci & MRSA
Staphylococcus infections
Penicillin
Anti-pseudomonal penicillin
mixed aerobic
& anaerobic
bacteria
Pseudomonas
aeruginosa
Gram positive
& negative
bacteria
Extended-spectrum
penicillin
Gram positive
cocci
(inc enterococci)
UTIs (inc E. coli)
respiratory tract
infections
(inc H. influenzae
Penicillin G
syphilis
streptococcal
infections
COMMON SIDE EFFECTS
STREPTOMYCIN
ETHAMBUTOL
NEUROPATHY : OPTIC NEURITIS
PYRAZINAMIDE
VOMITTING
RIFAMPIN
HEPATITIS
ISONIAZID
NEUROTOXICITY
HEPATOTOXICITY
QUINOLONE
TERATOGENIC (IN PREGNANCY)
BLOCKAGE OF POTASSIUM CHANNELS
CNS
DIZZINESS
HEADACHE
GI
DIARRHOEA
VOMITING
AMINOGLYCOSIDE
OTOTOXIC
CHLORAMPHENICOL
TOXICITY
DRUG INTERACTIONS
WARFARIN
PHENYTOIN
GRAY BABY SYNDROME
CARDIOVASCULAR COLLAPSE
CYANOSIS
DECREASED RBC
INHIBITION OF RED CELL MATURATION
GASTROINTESTINAL
SUPERINFECTIONS
TRIMETHOPRIM
STEVEN-JOHNSON SYNDROME
GI DISTURBANCES
TETRACYCLINES
RENAL TOXICITY
SUPERINFECTION , EG: CANDIDIASIS
GASTROINTESTINAL : IRRITATIVE REACTION
TOOTH PIGMENTATION
ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA
HAEMATOLOGIC : EOSINOPHILIA
FUSIDIC ACID
JAUNDICE
CLINDAMYCIN
COLITIS
SEVERE DIARRHEA
ERYTHROMYCIN
INHIBITS HEPATICE METABOLISM OF WARFARIN, DIGOXIN
CHOLESTATIC HEPATITIS
ABDOMINAL CRAMPS, NAUSEA, VOMITING,DIARRHOEA
GLYCOPEPTIDES
RED MAN SYNDROME
NEUTROPENIA
OTOTOXICITY
SIDE EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS
CARBAPENEM
SEIZURES
NAUSEA
ALLERGIC REACTIONS
CEPHALOSPORIN
DEVELOPMENT OF SECONDARY INFECTIONS
NEPHROTOXICITY
GASTROINTESTINAL IRRITATIONS
PENICILLIN
BLACK HAIRY TONGUE (CHRONIC)
NEPHROTOXIC
ALLERGIC REACTION
MECHANISM OF INFECTION
BETA LACTAMS- MECHANISM OF ACTION AND RESISTANCE
ANTIBIOTICS-MECHANISM OF ACTION
HOW ANTIBIOTICS WORK
MECHANISMS
INHIBITION OF BACTERIAL ENZYMES/METABOLIC PATHWAYS
INHIBITION OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
INHIBITION OF NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS
INHIBITION OF CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTION
INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS