von tariro nhandara Vor 2 Jahren
209
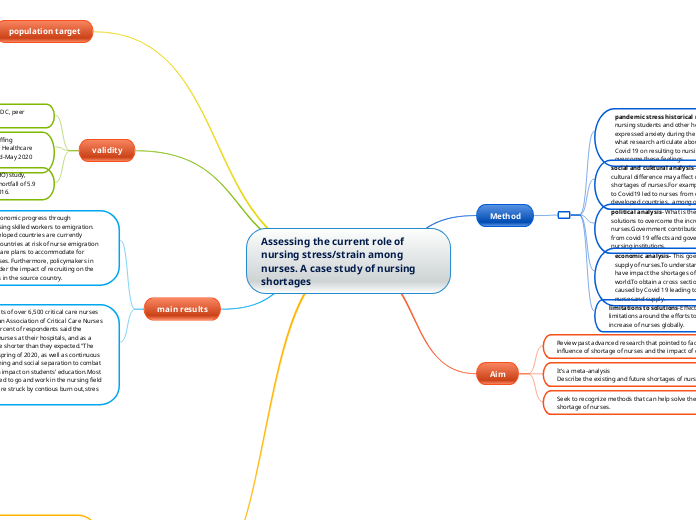
Assessing the current role of nursing stress/strain among nurses. A case study of nursing shortages
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the nursing profession, leading to increased stress and anxiety among healthcare workers. This situation has exacerbated existing nursing shortages, especially in developed countries.