von Namgyel Ohm Vor 1 Jahr
157
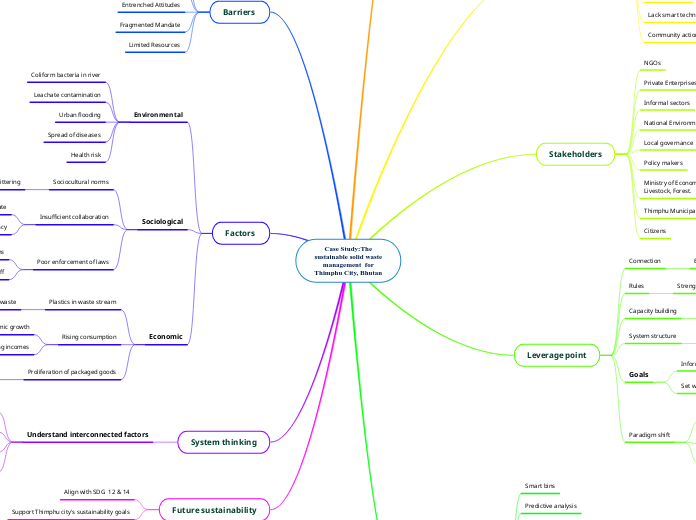
Case Study:Thesustainable solid wastemanagement forThimphu City, Bhutan
Efforts to manage solid waste sustainably in Thimphu City, Bhutan, revolve around a comprehensive approach integrating multiple facets such as economic, environmental, and sociocultural factors.