Theresa Ton tt26827
Essence Hines ECH2748
Leslie Robles ldr2374
Candy Pan cp38975
release factor
free polypeptide
destination in cell
targeting polypeptide to specific locations
ER lumen
golgi
chemical modifications
transported
plasma membrane
lysosomes
back to ER
free ribosome in cytosol
SRP binds & attaches
bound ribosome
enzyme signal peptidase
folds into final conformation
termination
Translation
codons
code for a specific amino acid
amino acid codes
tRNA base pairs its anti codon with mRNA starting sequence
translation initiation complex (In large ribosomal subunit)
tRNA goes from A site to P site
modified amino acid f-MET
codon recognition
peptide bond formation
translocation
mRNA goes to cytoplasm
mRNA has a 5' cap & 3' poly A tail
Ribosomal subunits
mRNA moves through ribosomes one codon at a time
amino acids attach to proper tRNA's with help of specific enzyme
aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
P, E, & A site
polypeptide leaves ribosome
protein & RNA
promoter
RNAP
RNA synthesis
5' to 3'/Downstream
snRNA
RNA polymerase ||
RNA polymerase
microRNA
pre mRNA
the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA
Termination
Poly site A
5' CAP
Elongation
Initiation
Transcription
Gene Regulation
Specific transcription factors
Distal control elements
Enhancer
Allow activators or repressors bind
Does not allow for binding of general transcription factors and RNA Polymerase II
Attachment of general transcription factors and RNA Polymerase II
Basal/background expression
High transcription
Proximal control elements
Prokaryotes
Operator
Repressor
Do not allow RNA polymerase to bind
No transcription of genes
Activator
Allow RNA polymerase to bind
Transcription of genes
Control access of RNA Polymerase
Operons/lac operons
Lactose absent
Repressor active, RNA Polymerase cannot bind and no trasncription of DNA
Lactose present
No glucose
Production of cAMP that binds to CAP that helps RNA polymerase bind to promoter and transcription of DNA
Glucose present
No cAMP made to activate CAP so no binding of RNA polymerase and no DNA transcription
Repressor is inactive, RNA polymerase binds and transcription of DNA
Regulatory genes
lac a
Transacetylase
lac Y
Permease
lac Z
β-galactosidase
Histone acetylation
Histone
Histone core
H1
2 H2A, 2 H2B, 2 H3, 2 H4
Condensation of chromatin/reduced transcription
Promotes transcription by opening up chromatin structure
3 ATP
6 NADPH
6 ATP
Water donates 2 e-
Photosynthesis
CAM plants
light reaction at day, Calvin Cycle at night
C4 plants
CO2 fixed in mesophyll cells and Calvin cycle in bundle-sheath
C3 plants
Photorespiration
Rubisco binds to O2
Carbon Cycle/light dependent
3 CO2 attaches to RuBP with Rubisco to form 6 3-phosphoglycerate
Phase 2: Reduction
6 G3P
Phase 3: Regeneration of CO2 Acceptor (RuBP)
RuBP
3 ADP
6 NADP+ and 6 phosphate groups
6 ADP
Light reaction
Photons hit pigment molecules and excite it and causes other pigment molecules around it to get excited to higher energy level
e- transferred from excited P680 to primary e- acceptor
Electric transport chain
Photon hit pigment molecules and excites and excites nearby pigment molecules
e- transferred from P700 to primary e- acceptor
2nd Electron transport chain
NADPH
ATP
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Water is oxidized
CO2 is reduced
signal molecule hydrophilic (1st messenger)
ion channel receptor
Tyrosine Kinase receptor
G protein linked receptor
cAMP (second messenger)
CELL COMMUNICATION
by physical contact
by releasing a signal
stages of signaling
transduction
protein kinases
transfer of pi from ATP
phosphatase
removal of pi from proteins via hydrolysis
Response
triggering of phosphorylation cascade
last kinase enters nucleus
transcrip. of specific gene
synthesis of particular protein in cytoplasm
Reception
signal receptor proteins
tyrosine kinase receptor
inactive tyrosine dimer
activated dimer
intracellular signal proteins
activated proteins
intracellular signal pathway
ligand-gated ion channel
specific ions flow through
cellular response
channel closes
GPCR (transmembrane)
G protein
activation of G protein
Adenylyl Cyclase
cAMP
activates another protein
Phosphorylation Cascade
Critical players in signaling
receptors
ligands
intracellular
steroid hormone
hormone passes through membrane
mRNA translated to specific protein
stimulation of gene into mRNA
hormone-receptor complex binds to genes
hormone binds to receptor protein in cytoplasm: activating it
membrane
help of molecules from inside
second messenger (help surface receptor)
Plasma membrane
Selective permeability
Ions
Large, uncharged polar molecules
Small, uncharged polar molecules
Small, nonpolar molecules
Mosaic plasma membrane
Transmembrane proteins
Functions
Intercellular joining
Transport
Channel proteins
Aquaporin
Protein pumps
Electrogenic pumps
Proton pump
Sodium-Potassium pump
Active transport
Cotransport
H+/sucrose cotransporter
Bulk transport
Endocytosis
Receptor-mediated
Pinocytosis
Exocytosis
Carrier proteins
Passive transport
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Water balance
Tonicity
Hypotonic
Turgid
Lysed
Hypertonic
Shriveled
Plasmolyzed
Isotonic
Flaccid
Attachment to ECM & cytoskeleton
Signal transduction
Cell-cell recognition
Enzymatic activity
Peripheral proteins
Integral proteins
Fibronectin
Collagen fiber
Proteoglycan complex
Extracellular fluid
Phospholipid bilayer
Polysaccharide molecule
Proteoglycan molecules
Core protein
Cholesterol
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic/hydrocarbon tails
Fluid
Viscous
Gel phase/rigid
Liquid crystaline/fluid phase
2 ATP used
ATP is made
NADH+ made
ATP made
Water made
NAD+ used
Pyruvate used
2 Acetyl CoA formed
NADH formed
1 FADH2 made
3 NADH used
1 Acetyl CoA makes 1 ATP,3 NADH,
Step 1:Acetyl CoA interact with
Oxaloacetate to form
Citrate
Step 3: Isocitrate is oxidized to form alpha Ketoglutarate
NADH and FADH2 is made
No ATP used but 1 made
2 pyruvate
Pyruvate oxidation
Glycolysis
Mitochondria
Citric Acid Cycle
Glucose
ATP used
CO2 formed
Molecules involved with Cellular Respiration
Concept Map 2
store and transports genetic info
provide energy
protecting organelles
saturated
unsaturated
Liquid at room temperature
fats and oils
fat layers
phospholipids
steriods
energy storage
sparing proteins and fat
building macromolecules
Energy production
messager
building tissues
collagen
repairing
structural
maintain pH
immune system
transport/storage
enzymes
anti body
nucleic acids
lipids
carbohydrates
proteins
Biomolecules
Functions of molecules in organisms
ech2748
Essence Hines
Alternate Splicing: exons can be put together in any order
Regular Splicing: exons stay in their natural order
Exons are spliced together with a 5'CAP and 3' poly-A tail at it ends
Introns are cut out
RNA Splicing
3' poly-A tail
3' end
newly made RNA elongates
Can function as
catalyst called ribozyme
Self-replicates & stores genetic information about vesicle
Protocell "daughters"
Prokaryotes
Pili
Fimbriae
Nutritional Modes
Light
Photoautotroph
Photoheterotroph
CO2, HCO3-, or
related compound
Organic compounds
Inorganic chemicals
Chemoautotrophs
Capsules (Slime layers)
Metabolism
Obligate aerobes
Obligate anaerobes
Facultative anaerobes
Ribosomes
Eukaryotes
Cytoskeleton
Microfilaments
Cortex
Inner cytoplasm
Extending pseudopodium
Cell division
Changes in cell shape
Cytoplasmic streaming
Parallel actin filaments
Myosin motor protein
Muscle contraction
Microtubules
Chromosome movements
in cell division
Organelle movement
Motor protein
Kinesin
Vesicle
Cell motility
Cilia & flagella
Proteins between microtubules
Intermediate filaments
Anchorage of nucleus
& certain other organelles
Formation of nuclear lamina
Maintains cell shape
Membrane-bound organelles
Endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Nucleus
Chromatin
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope
Lysosomes
Autophagy
Phagocytosis
Golgi apparatus
Peroxisome
Food vacuoles
Mitochondrion
Cellular Respiration
30-32 ATP
Lactic acid fermentation
2 lactate
Alcoholic fermentation
2 Acetaldehyde
2 ethanol
Glycolysis
Energy payoff stage
4 ATP
Energy investment stage
2 NADH
Pyruvate Oxidation
Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle
2 ATP
2 FADH2
6 NADH
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
26-28 ATP
Electron transport chain
Proton-motive force
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP and heat)
Oxygen is reduced
Glucose is oxidized
Plant cells
Central vacuole
Plasmodesmata
Chloroplasts
Animal cells
Centrosomes
Cell junctions
Tight junctions
Desmosomes
Gap junctions
Extracellular matrix
Archaea
Extremophiles
Methanogens
Extreme halophiles
Extreme thermophiles
Bacteria
Endospores
Cell wall
Polysaccharides & proteins
Peptidoglycan
Nucleoid
Plasmids
Flagella
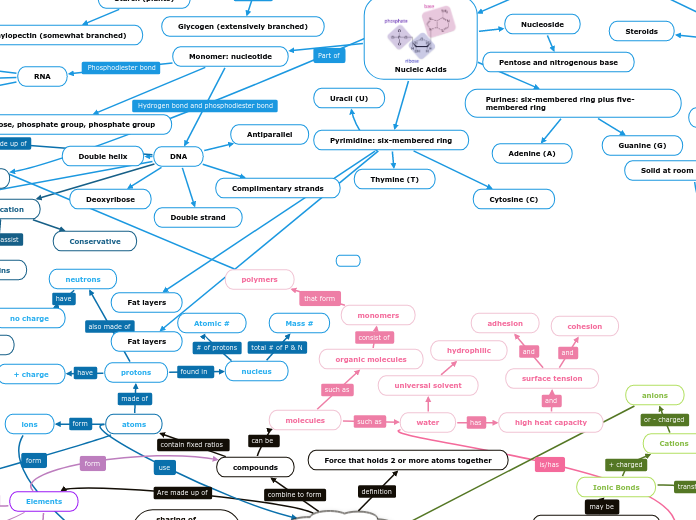
Biological Molecules
Nucleic Acids
Purines: six-membered ring plus five-membered ring
Guanine (G)
Adenine (A)
Pyrimidine: six-membered ring
Fat layers
Uracil (U)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Nucleoside
Pentose and nitrogenous base
Monomer: nucleotide
RNA
Ribose
Single strand
Pentose, phosphate group, phosphate group
DNA
Complimentary strands
Deoxyribose
Antiparallel
Replication
Conservative
Helicase
Primase
DNA ligase
DNA polymerases
DNA pol I
DNA pol III
Leading strand
Lagging strand
Okazaki fragments
Single-strand binding proteins
Topoimerase
Origins of replication
Replication fork
Daughter strands
Parent strands
Genes
Chromosomes
Double helix
Double strand
Proteins
Primary struture
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
R group interactions
Multiple polypeptides
Covalent (disulfide bridge)
Hydrogen
Ionic
Hydrophobic interactions
Interactions between R groups
Bond: hydrogen bond
β pleated sheets
α helix
Dictates second and tertiary structure
Bonds: covalent and peptide
Amino acid change
Monomer: amino acid
Polymer: polypeptide
α carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, R group (side chain), hydrogen
Lipids
Steroids
Phospholipids
Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Made up of glycerol joined by 2 fatty acids and phosphate
Amphipathic
Serves as energy
Mostly hydrocarbons
Nonpolar/Hydrophobic
Fat (triacylglycerol/triglyceride)
Unsaturated fat
Trans fat
formed artificially during hydrogenation
cis double bond (kink)
Saturated fat
Flexible molecule
Solid at room temperature
Fatty acid
Carbohydrates
Ketose
Aldose
Structural polysaccharide
Chitin
Cellulose
Storage polysaccharide
Glycogen (extensively branched)
Dextran
Starch (plants)
Amylopectin (somewhat branched)
Amylose (unbranched)
Serves as energy source
carboxyl group with many hydroxyl groups
Monomer: Monosaccharide
Polymer: Disaccharide or Polysaccharide
3 or more monosaccharide
2 monosaccharide
Strongest bonds in dry compounds!! (known as salts, which may form crystals)
Ionic Bonds
Valence electrons b/w atoms
Cations
anions
Weak chemical interactions
Van der Waals
2 nonpolar covalent bonds
atoms are close together; very weak
hydrogen bonds
2 polar molecules/bonds
dipole-dipole
attraction b/w partial + & partial - of 2 molecules
polar covalent bonds
electrons not shared equally
Electronegativity is when something is an interactive property & the more EN an atom is the more strongly it pulls electrons to itself
covalent bonds
Valence
Single bond
Double bond
Triple bond
nonpolar covalent bonds
electrons shared equally & same EN
hydrophobic
Energy levels
Electrons
orbitals
energy
negative charge
polymers
Chemical Bonds
compounds
atoms
protons
nucleus
Atomic #
Mass #
+ charge
no charge
ions
molecules
water
high heat capacity
surface tension
adhesion
cohesion
universal solvent
hydrophilic
organic molecules
monomers
Force that holds 2 or more atoms together
types of chemical bonds
chemical reactions
Chemical equilibrium
reactants
products
sharing of electrons b/w atoms in molecules
Elements
chemical behavior
# of electrons
valence shells
valence electrons
Radioactive Isotopes
Isotopes
neutrons
RNA moves downstream the DNA to continue transcription