Mesolimbic Pathway Mindmap
Domperidone
Renal
Dose reduction
Liver
Aromatic hydroxylation
N-dealkylation
PT2448
Mechanism of action
Dual mechanism of action
Domperidone acts as an antagonist at the dopamine D2 receptors in the CTZ.
By inhibiting agonist activity in the CTZ it will not VC.
CTZ
Decreases excitatory input in vomiting centre
Decreases sensitivity to noxious stimuli
Peripherally
Gastrokinetic
Domperidone
Domperidone-N-oxyde
Indications
Rx use
Nausea and vomiting induced by
Migraine
Drugs
Medications to treat Parkinson's disease
Conditions
Cystic fibrosis
GORD
PF3012
Post-operative
Chemotherapy
OTC use
Pharmacist only supply
- Pharmacist only consultation
- Data from 2014-2016 highlighted that Domperidone was inappropriately supplied to patients
PF1011
Monitoring
- This black triangle is a visual prompt for healthcare professionals.
- It is to highlight that this medicine is associated with additional monitoring to allow continued risk vs benefit analysis.
- Any healthcare professional is to report any suspect adverse drug reaction.
- Any reporting can be made through the HPRA using the reporting system.
- Due to the safety concerns, the pharmacist must be directly involved in the decision to supply the medicine to a patient.
QT interval prolongation
- Domperidone is associated with QT interval prolongation
- There is a greater risk in adults > 60 years of age
- Risk is also associated with patients taking other QT-interval prolonging drugs such as Olanzapine, fluoroquinolones, Amiodarone.
- Electrolyte imbalances such as hypomagnesemia and hypokalaemia can predispose patients to QT interval prolongation
Relief of nausea and vomiting only
No longer used for bloating or heartburn
Maximum of one week
Formulation
Counselling points
- Signs and symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia such as dizziness, heart palpitations and fainting
- common side effects such as dry mouth
- uncommon side effects headache, diarrhoea, rash, pruritus
- Hyperprolactinaemia is a side effect
- Domperidone can be exploited for this side effect and has an unlicensed as a galatagogue
- PF2014 breast feeding highlighted this use
- It can be used in mothers with pre-term babies and insufficient milk supply
Motillium
Oral suspension 1mg/ml
Oro-dispersible tablet
Film coated tablet
Olanzapine Structure
N-Desmethylolanzapine
Olanzapine
Olanzapine Mindap
Chemical structure
Metabolism
Counselling
- Reduced doses required for renal/ hepatic impairment
- Smoking induces metabolism- alter dose accordingly
Hepatic (40%)
Glucuronidation
Olanzapine 10-N-Glucuronide
Oxidation
N-Desmethylolanzapine
Mechanism of Action
Alpha -1 Antagonist
Postural Hypotension
Sedation
5HT2C Antagonism
Weight Gain
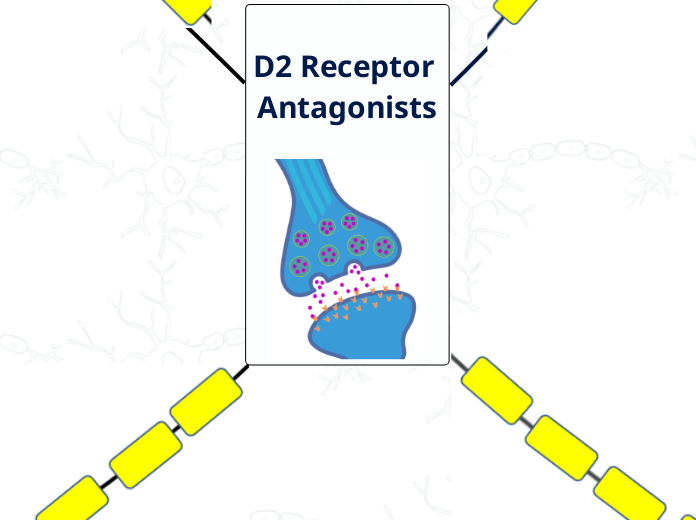
D2 Receptor Antagonism
Counselling
- Avoid in pregnancy unless the benefit outweighs the risk
- Avoid breastfeeding unless the benefit outweighs risk
- Avoid direct sunlight- causes photosensitivity at high doses
- C/I in patients < 18 years
- Risk of developing neuromalignant syndrome
Chemotherapy Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Pf6420
Off-licence
Preventing reoccurrence of bipolar
Schizophrenia
Agitation
Disturbed Behaviour
Mania
Moderate to Severe Manic episodes
Formulations
Olanzapine Embonate
IM injection
Olanzapine
Specially Manufactured
Oro Dispersible
Haloperidol
Mechanism of Action
Alpha-1 Antagonism
Postural Hypotension
Sedation
Drowsiness – Take before bed, do not drive or operate machinery, be aware when drinking alcohol.
D2 Antagonism
Tuberoinfundibular
Hyperprolactinaemia
Nigrostriatal
EPSEs
Mesocortical
Negative Symptoms
Mesolimbic
Positive Symptoms
Metabolism
The influence of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of haloperidol has not been evaluated. No dose adjustment is recommended, but caution is advised when treating patients with renal impairment. However, patients with severe renal impairment may require a lower initial dose, with further doses administered and adjusted according to the patient’s response
The influence of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of haloperidol has not been evaluated. Since haloperidol is extensively metabolised in the liver, it is recommended to halve the initial dose.
The recommended initial haloperidol dose in elderly patients is half the lowest adult dose. Further doses may be administered and adjusted according to the patient’s response. Careful and gradual dose uptitration in elderly patients is recommended.
Hepatic
PF2448
Glucuronidation
Oxidative N-dealkylation
Ketone Reduction
Chemical Structure
Haloperidol Structure
3-(4-fluorobenzoyl) propionic acid
4-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-piperidinol
Indications
Monitoring:
Electrolyte disturbances such as hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia increase the risk for ventricular arrhythmias and must be corrected before treatment with haloperidol is started. Therefore, baseline and periodic electrolyte monitoring is recommended
Counselling:
- Avoid in pregnancy unless the benefit outweighs the risk
- Avoid breastfeeding unless the benefit outweighs risk
- C/I in patients < 18 years
- Risk of developing neuromalignant syndrome
PF4014
Huntingtons Disease
Tic Disorders
Persistent Aggression
Vascular Dementia
Alzeimhers Dementia
Nausea & Vomiting
Combination Treatment (Alternative Treatment Ineffective)
Palliative Care N+V
Prophylactic Post-Operative N+V
Acute Delirium
Schizophrenia
Bipolar 1 Disorder
Moderate to severe manic episodes
Switch from mania to depression: There is a risk in the treatment of manic episodes of bipolar disorder for patients to switch from mania to depression. Monitoring of patients for the switch to a depressive episode with the accompanying risks such as suicidal behaviour is important in order to intervene when such switches occur.
Acute psychomotor agitation
Formulation
PF1012
Haloperidol Decanoate
Monitoring:
A baseline ECG is recommended before intramuscular dosing. During therapy, the need for ECG monitoring for QTc interval prolongation and for ventricular arrhythmias must be assessed in all patients, but continuous ECG monitoring is recommended for repeated intramuscular doses. ECG monitoring is recommended up to 6 hours after administration of haloperidol solution for injection to patients for prophylaxis or treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Whilst on therapy, it is recommended to reduce the dose if QTc is prolonged, but haloperidol must be discontinued if the QTc exceeds 500 ms.
IM Depot Injection
PF3010
Greater risk of QT prolongation with use of IM depot injectable dosage forms of haloperidol.
Oral Concentrate
Counselling:
Oral solution and suspensions need to be shaken before use.
Tablet
Haloperidol Lactate
IV Injection
Licensed in Ireland
D2 Receptor Antagonists