von GEORGE CARJAC Vor 1 Tag
11
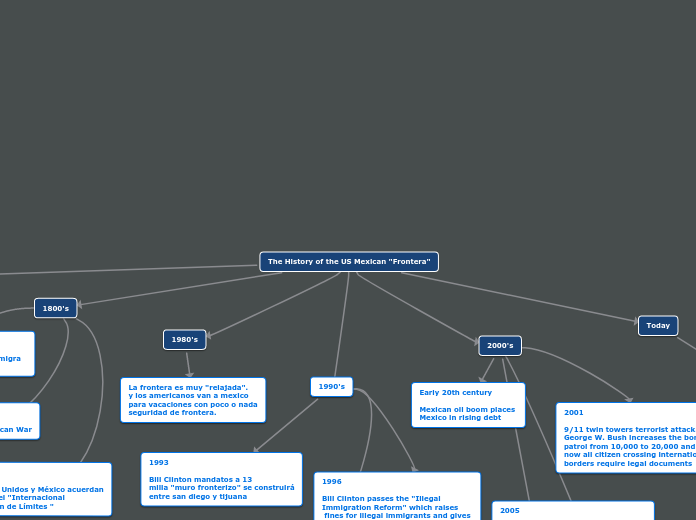
History Timeline
The period following the Civil War in the U.S. marked a time of rebuilding and reconciliation. In Canada, significant developments were taking place, such as the completion of the Canadian Pacific Railway in 1885, which became the country'