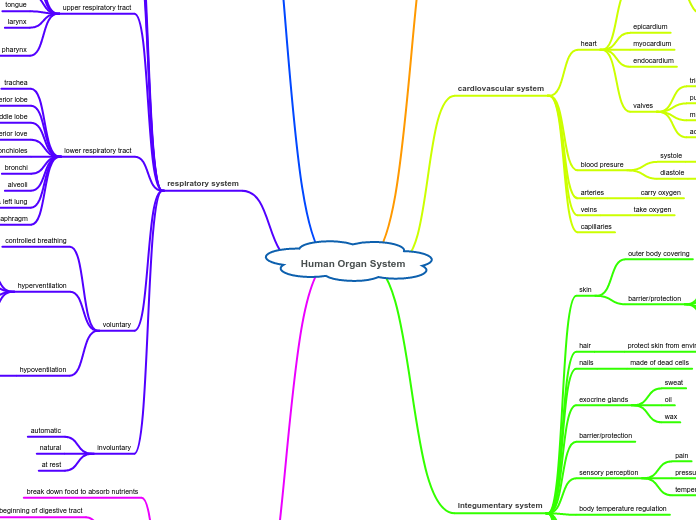
Human Organ System
digestive system
gallbladder
stores and concentrates bile from liver
liver
makes bile
pancreas
gland organ
large intestine
anus
rectum
sigmoid colon
cecum
get rid of waste
small intestine
duodenum: firest section
nutrients absorption
stomach
hollow organ or container, that holds food
enzymes & acids
esophagus
receives food when swallow
mouth
ingestion
saliva breaks down food
chew into smaller pieces
food into mouth
beginning of digestive tract
break down food to absorb nutrients
respiratory system
involuntary
at rest
natural
automatic
voluntary
hypoventilation
caused by
obesity
chronic lung diseases
medication
opioids
illegal drugs
alcohol
hyperventilation
chest pain
syncope
numbness & tingling in hand/feet
light headness
controlled breathing
lower respiratory tract
diaphragm
large done-shaped muscle
right & left lung
alveoli
bronchi
bronchioles
inferior love
middle lobe
superior lobe
trachea
upper respiratory tract
pharynx
hollow structure, entry for esophagus
near nose and ends at trachea
larynx
tongue
oral cavity
nostril
nasal cavity
removes CO2 from blood and releases from body
moves oxygen through your body
brings in oxygen in lungs
neurological system
peripheral nervous system
somatic nervous system
motor (efferent)
sensory output
sensory (afferent)
sensory input
autonomic nervous system
parasympathetic division
calming response
sympathetic division
arousing response
central nervous system (CNS)
spinal cord
main office/command control of body
brain
4 lobes
occipital
temporal
partietal
frontal
integumentary system
2 main types of glands
sebaceous gland (oil gland)
sudoriferous (sweat gland)
layers of skin
hypodermis
dermis
epidermis
skin colour
melanin
production of vitamin D
excretion
absorption
storage
salt
vitamins
water
glucose
fat
body temperature regulation
sensory perception
temperature
pressure
pain
exocrine glands
wax
oil
sweat
nails
made of dead cells
hair
protect skin from environment
skin
barrier/protection
physical damage
UV light
diease
chemicals
outer body covering
cardiovascular system
capillaries
veins
take oxygen
arteries
carry oxygen
blood presure
diastole
relaxation
systole
contraction
valves
aortic valve
mitral valve
pulmonary valve
tricuspid valve
endocardium
epicardium
4 chambers
right ventricle
left ventricle
right atrium
left atrium
musculoskeletal system
skeletal system
framework of body
mechanical basis for movement
bones, joint, associated tissues
muscles system
joint stabilization
movement production
skeletal muscles and tendons
smooth muscle
walls of blood vessels and hollow organs
skeletal muscle
striated
attached to bones
cardiac muscle
non-striated
myocardium
heart