von Tulsiani Megha Vor 1 Tag
41
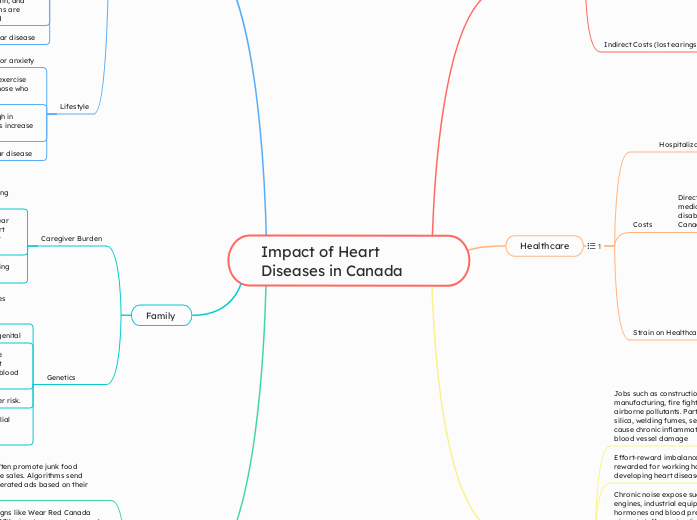
Impact of Heart Diseases in Canada
Heart disease remains a significant health issue in Canada, impacting individuals and families alike. Genetic factors, such as familial hypercholesterolemia and Type 2 Diabetes, play a crucial role in increasing the risk of heart disease, with specific ethnic groups like Africans and South Asians being more susceptible.