von Adrianna Maertens Vor 4 Jahren
237
Indigenous Studies Unit 1
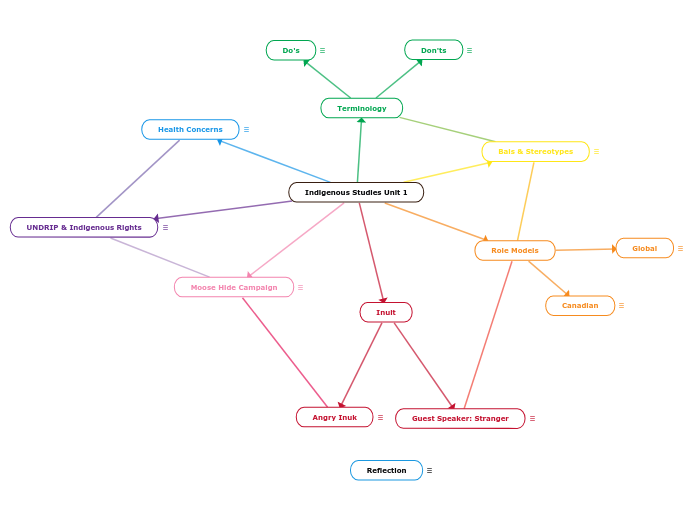
von Adrianna Maertens Vor 4 Jahren
237

Mehr dazu
My Learning:
Challenges Indigenous People Face:
The Path Forward: