Introductory Biology II concept Map
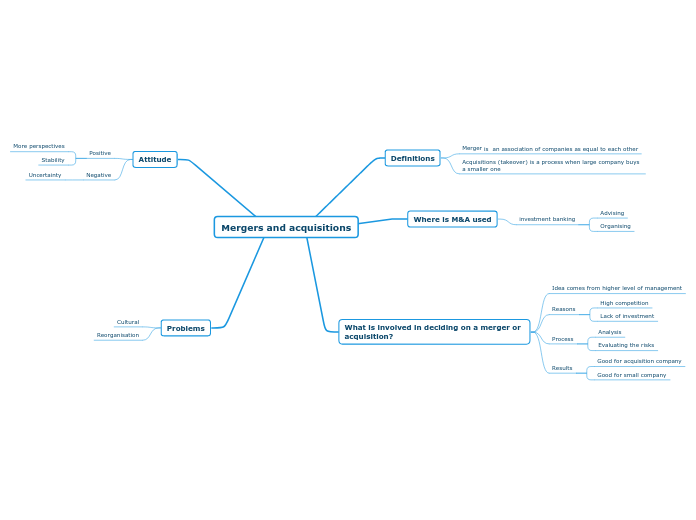
Population Regulation
What we do to control
the population ourselves:
Smoking
Obesity
Alcohol Use
Automobile accidents
Suicides
AIDS
Homicides
War
Key:
Red: Exam 1
Yellow: Exam 2
Blue: Exam 3
I expanded the most on the areas I needed the most review.
Dieases help contrrol
our population growth
Measles
Tuberculosis
Small Pox
Flu
Resources are limited and limiting on population growth.
Food
Water
Air Quality
Lliving Space
Biological Control of
Pests:
Hormonal
control
Pheromone
stations
Pheromone
traps
Reproductive
control
Release
Sterile
males
Chemical
Sterilants
Release
incompatible
pest stains
Control by
another
organism
Parasites
Predators
Pathogens
Population Growth
A population is a group
of interbreeding individuals
of the same species in a
particular site.
Steady population growth depends on
a balance between growth factors and
environmental resistance factors like:
Unsuitable or destroyed
habitat (-)
Adequate Food
Supply (+)
Specialized Niche(-)
Generalized Niche (+)
Low reproductive rate (-)
High reproductive Rate (+)
The environment (including
other species present therefore
competition)plays a major role
in the growth of a population.
Competitive Exclusion Principle:
When similiar species that compete
for the same limiting resources cannot
coexist in the same environment (if their
niches are identical.) One will use the
resources more efficiently and thus reproduce
more rapidly. Even a slight reproductive advantage
will eventually lead to local elimination of the
inferior competitor.
OR a species can evolve through natural selction
to use a different set of resources/niche to avoid
competition and coexist. (each species K value is lower)
The Logistic growth of a
population is s-shape and
takes into account how many
individuals of the same species
can be supported by the
environment (carrying capacity (k).)
Not all species have the
same carrying capacity
because every species
interacts with the environment
in a different way.
Adaptive Radiation
Adaptive Radiation is
the development of several
new species from a common
ancestor due to adaptations
to different environments.
Remember that all species arise
from preexisting species.
Adaptive radiation is pretty similiar
to divergent evolution the only difference
is that the radiation happens all at the same time.
Contemporary Extinction:
Habitat Destruction
Overgrazing
Farming
Deforestation
Hunting
Over exploitation
Species Introductions
Introduces new diseases
Increase Predation
Increase Competition
Hybridization
Inbreeding
Speciation
Species are groups of (reproductively
isolated) actually or potentially
interbreeding (therefore gene flow occurs)
populations.
As divergent evolution
occurs (the accumulation
of phenotypic differences
between 2 lineages originating
from a common ancestor over
time) the two lineages eventually
become different species that are
unable to exchange genes.
Divergent Evolution occurs
with character displacement
over time.
Character displacement refers
to the phenomenon where differences
amoung similiar species whose distributions
overlap geographicallyare accentuated in
regions where the species co-occur to reduce
competition.
However, Sometimes (1% of the time)
two species are able to mate and produce
a hybrid species.
This can create a hybrid
that is considered Polyploidy.
Can also be cause by a
nondisjunction of chromosomes
of one parents chromosome in
their gamete thereby producing
a polyploidy when combined with
a normal gamete.
Can be caused by an unreduced
gamete and a normal gamete
coming together to form a triploid
gamete or a new species.
Allopatric Speciation:
species formation from a
common ancestor in
geographically separate locations
(therefore it occurs in isolation.)
Migration
Migration is the movement
of genes between populations.
Migration tends to eliminate
existing genetic differences
between populations.
Allele frequencies change
in the direction of the donor
/source population due to
migration.
Hardy Weinburg
Equation cannot
be used to calculate
the allele or genotype
frequencies if this occurs.
Migration Rate:
the proportion of immigrants
in a population after migration.
Therefore: Migration rate
is the number of immigrants
divided by the new total population.
If we know the migration rate,
we can find out migration rate of alleles.
Q(after immigration)=
q ((the recessive allele frequency)of immigrants) M(migration rate)+q (residents)
To find P just subtract the new q value from 1.
Because p+q=1
Mutation and Genetic Drift
Genetic Drift is the
random changes/
deviations in allele
frequncies in a population
from generation to
generation.
Can be a result of
the genetic bottleneck
effect.
Genetic Bottleneck Effect:
Random changes in
allele frequencies in
a population due to a
dramatic reduction in
population size.
A result of sampling error
in a population of limited
size.
Sampling error is the
random deviation from
the expected value
determined by chance
Therefore, the larger the population/
sample size the smaller the deviation
on average.
Genetic drift involves
colonization thus creating
the founder effect.
Founder Effect: Random
changes in allele frequencies
in a population during
colonization.
It's basically the colonizer's
chance of deviation from the
gene frequencies of their
source population.
A mutation is a
random change
in the genetic
code.
Every locus has a
different mutation
rate.
Mutations are where
new alleles come from
Mutations are the
ultimate source of
genetic variation.
Mutations are considered
good or bad based on their
environment.
Selection
Natural Selection operates in
human populations to ensure
the reduced survival and minimal
reproductive potential of inferior
species.
ensures minimal reproductive potential
by making most mutants infertile or sterile.
So only the superior/most able-bodied species
survive.
Selection Differential:
The difference between
the mean of the population
and the mean of individuals
selected to be the parents of
the next generation.
Therefore:
Selection Differential=
Mean(selected)-Mean (whole)=
Mean intensity of selection.
Selection as defined
by Dr. Levin: Differential
reproduction amoung
differing phenotypes in a
population.
Selection is basically
the only form that
produces adaptive
evolutionary changes
for a population. It is
the only way for a
populaiton to improve.
There are many different
kinds of selction.
Artificial Selection: Modification
of a species by human intervention
so that certain desirable traits are
represented in successive generations.
Influenced by the heritability
of the trait and the pressure/
force that the breeder uses.
Stabilizing Selection:
Genetic diversity decreases
as the population stabilizes on
a particular trait, the intermediate
is favored.
Disruptive Selection:
changes in population
genetics in which extreme
values for a trait are favored
over intermediate values.
Directional Selection:
When a single phenotype
is favored causing allele
frequency to continually
shift in one direction.
Environmentally Dependent
The Chromosome Complement
Chromosomes are the visible bodies
within dividing cells that contain DNA
and thus carry genetic information.
Humans are diploid,
meaning we have 2 sets (2n)
of chromosomes therefore, 23 pairs
of chomosomes.
We get one chromosome
set from each of our parents.
This is made possible through
Meiosis which is a 2 stage type
of cell division in sexually
reproducing cells that results
in half the chromosome number
than the parent.
Sometimes there are
alterations in the chromosome
number that cause genetic disorders
like Down Syndrome (trisomy 21.)
Meitoic disjunction is when
members of a pair of homologous
chromosomes do not separate
during Meiosis I or sister chromatids
fail to separate during meiosis II.
Creates Monomy
Creates Trisomy
Dihybrid Cross:
crosses between 2 loci
that are both heterozygous.
Monozygotic Twins:
Share 100% of their
genes.
Dizygotic twins:
share 50% of their
genes.
Monohybrid cross:
crosses between genotypes
with one locus that are heter-
ozygous.
Both crosses give rise to a charactersitic
or phenotype
Quantitative traits: refer to the
phenotypes that vary in degree
because of polygenic effects ans
their environment. Theycan be
measured like body weight, IQ etc.
Therefore, genotype and the
environment effect phenotype.
The heritability of a trait is the proportion
of the phenotypic variation that is
genetically based. (range values: 0-1)
1: All differences
are genetically controlled.
0: All differences are
environmentally controlled.
Meiosis guarantees the
continuity of genetic information
from one generation to another.
Additionally, humans have 2
sex chromosomes
Male: XY
Female: XX