La construcción del modelo de negocio
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
El método Lean Starup
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
3. Aprender
Coraje
Experimentación propia
Pivotar o perseverar
2. Medir
Los pequeños
Aprendizaje vs optimización
Indicadores accionables vs vanidosos
Contabilidad de la innovación
1. Crear
Hipótesis de crecimiento
Hipótesis de creación de valor
Producto mínimo viable
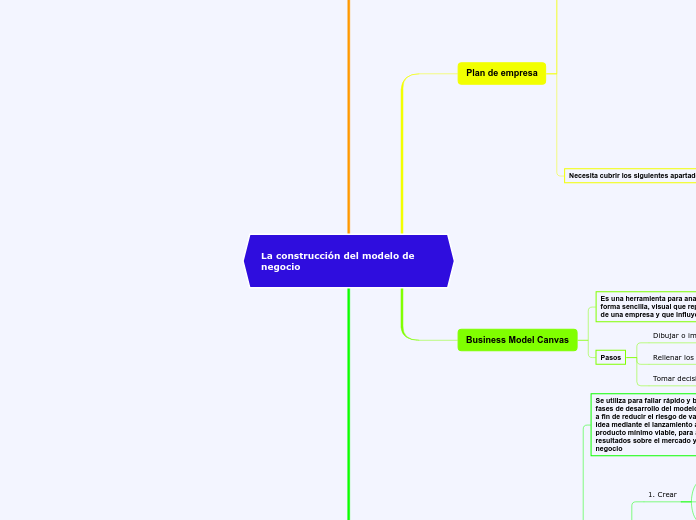
Se utiliza para fallar rápido y barato en las primeras fases de desarrollo del modelo de negocio startup, a fin de reducir el riesgo de validar de forma ágil la idea mediante el lanzamiento al mercado de un producto mínimo viable, para aprender con los resultados sobre el mercado y mejorar el modelo de negocio
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
He, They
Business Model Canvas
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Pasos
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
Tomar decisiones
Rellenar los nueve módulos del Canvas
Dibujar o imprimir lienzo Canvas
Es una herramienta para analizar en un lienzo de forma sencilla, visual que representa las áreas clave de una empresa y que influyen en su viabilidad
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
He is taller than she is.
Plan de empresa
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Necesita cubrir los siguientes apartados
Plan de marketing
Estudio de mercado
Cultura empresarial
Presentación de promotores
Presentación de la idea y proyecto
Trámites de constitución
Forma jurídica de la empresa y protección legal de la idea
Plan de inversiones y plan de financiación
Plan de recursos humanos y organización
Plan operativo
Aspectos dormales del plan de empresa
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Papel, impresión y encuadernación
Esquemas visuales
Elementos tipográficos que resalten
Márgenes adecuados y numeración
Estructura ordenada en epígrafes, con portada e índice
Redacción, ortografía y estilos cuidados
Información completa, breve, concisa y conveniente
Es el documento para planificar, evaluar y controlar los aspectos más importantes del negocio, desde la idea hasta los detalles más concretos relativo
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Mary, Paris
Definición
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Define qué ofrece la empresa al mercado, cómo lo va a conseguir, quién va a ser su público objetivo y cómo lo van a vender.
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
Create sentences
You have been practicing hard.