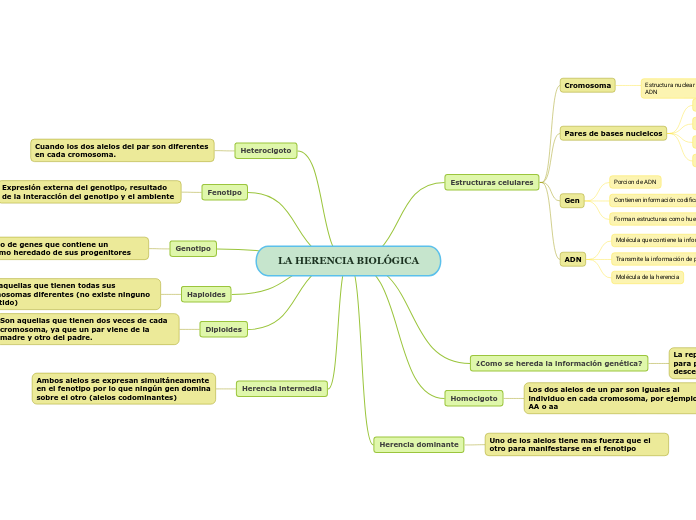
LA HERENCIA BIOLÓGICA
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
Herencia intermedia
Ambos alelos se expresan simultáneamente en el fenotipo por lo que ningún gen domina sobre el otro (alelos codominantes)
Diploides
Son aquellas que tienen dos veces de cada cromosoma, ya que un par viene de la madre y otro del padre.
Haploides
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
Son aquellas que tienen todas sus cromosomas diferentes (no existe ninguno repetido)
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
Genotipo
Conjunto de genes que contiene un organismo heredado de sus progenitores
Fenotipo
Expresión externa del genotipo, resultado de la interacción del genotipo y el ambiente
Heterocigoto
Cuando los dos alelos del par son diferentes en cada cromosoma.
Herencia dominante
Uno de los alelos tiene mas fuerza que el otro para manifestarse en el fenotipo
Homocigoto
Los dos alelos de un par son iguales al individuo en cada cromosoma, por ejemplo, AA o aa
¿Como se hereda la información genética?
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
La reproducción sexual tiene el potencial para producir la variación genética en la descendencia
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
Interogative form
Structure:
Did + subject + Base Form of the Verb?
e.g. Where did you meet her?
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Was I?Were you?Was he/she/it?Were we?Were you?Were they?
Form of word "to have":
Did I have?Did you have?Did he/she/it have?Did we have?Did you have?Did they have?
Negative form
Structure:
Subject + did not/didn’t + Base Form of the Verb
e.g. They didn’t like my food.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I was notYou were notHe/She/It was notWe were notYou were notThey were not
Form of word "to have":
I did not haveYou did not haveHe/She/It did not haveWe did not haveYou did not haveThey did not have
Affirmative form
Structure:
Subject + Verb in Past Simple (2nd form)
e.g. They lived in Spain three years ago.
Examples
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I wasYou wereHe/She/It wasWe wereYou wereThey were
Form of verb 'to have':
I hadYou hadHe/She/It hadWe hadYou hadThey had
Estructuras celulares
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
ADN
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
Molécula de la herencia
Structure:
Have/ has + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long has he been learning German?
Transmite la información de padres a hijos
Structure:
Subject + haven’t/hasn’t been + Verb-ING
e.g. She hasn’t been playing tennis for a long time.
Molécula que contiene la información genética
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
Gen
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
Forman estructuras como huesos
Structure:
Have/ has +Subject+ Past Participle?
e.g. Has she finished the letter?
Contienen información codificada para formar proteínas o ARN
Structure:
Subject + haven’t (have not)/ hasn’t (has not) + Past Participle
e.g. She hasn’t finished the letter.
Porcion de ADN
Structure:
Subject + have/ has + Past Participle (3rd Form of the Verb)
e.g. She has finished the letter.
Pares de bases nucleicos
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
Subtopic
Adenina
Structure:
BE + Subject + Verb-ING?
Are you eating now?
Guanina
Structure:
Subject + BE not + Verb-ING
e.g. You are not eating now.
Timina
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
Cromosoma
Estructura nuclear que corresponde al empaquetamiento del ADN
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.