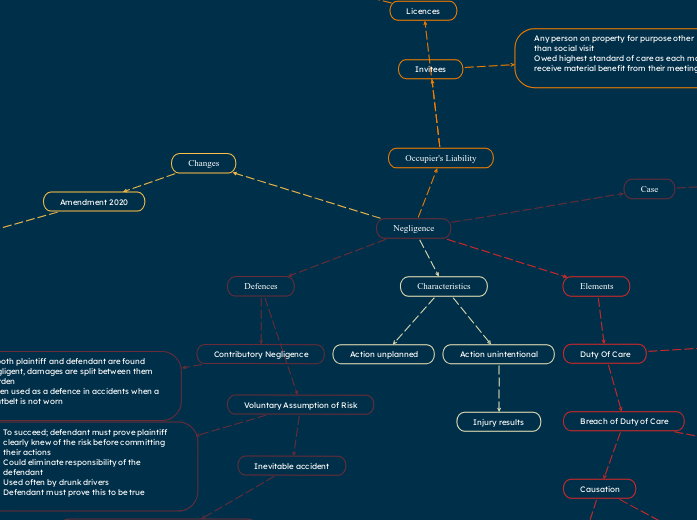
Negligence
Case
In this case the plaintiff was struck by a car while crossing the street between intersections. The car was backing up only moving 6km/hr The plaintiff claimed he did not hear or see the vehicle backing up. The vehicle allegedly reversed about 35 feet without the plaintiff noticing. The person driving the vehicle claimed to not see the plaintiff either while reversing. The judge ended up deciding that both parties were at fault because the crash could have been avoided if both parties showed care. This case is interesting because both parties were decidedly at fault.
Changes
Amendment 2020
In 2020 an amendment was made to the occupiers liability act. This amendment added a new section to include 'notice period' regarding snow and ice. The amendment states that " No action shall be brought for the recovery of damages for personal injury caused by snow or ice against a person or persons listed in subsection 2 unless, within 60 days after the occurrence of the injury, written notice of the claim...has been personally served on or sent by registered mail to at least one person listed in subsection 2".
Exceptions
If the plaintiff dies due to the injuries from the incident, the notice not being followed will not bar the action
Occupier's Liability
Licences
Trespassers
Enters property without permission or legal rights
Cannot deliberately harm and must exercise a reasonable standard of care
Trespassing children have special rights; must take steps to ensure reasonable precaution have been taken to protect allurements
Enters property wit implied permission of occupier
Lesser standard of care owed
Invitees
Any person on property for purpose other than social visit
Owed highest standard of care as each may receive material benefit from their meeting
Elements
Duty Of Care
-Did the defendant owe plaintiff duty of care
-This means that all reasonable precautions are taken to ensure no one or their property are harmed by your actions
Breach of Duty of Care
-Once duty established, court determines how much care defendant should have taken
-Standard of care is what care a reasonable person would take
-Can be found negligent even if obeying the law
-Children under 6 or 7 not seen as understanding consequences; not liable
-Standard for older children is similar to adults
-Minors involved in adult activities expected to meet adult standards
-Foreseeability: Would a reasonable person have foreseen said actions could have led to injury
Causation
-After courts determine that standard of care has been breached, plaintiff has to prove defendant was the cause of said injury
-Remoteness: how direct is the link or distance between action and injury
Actual Harm or Loss
-Legal action unsuccessful unless this final element can be proven
-Actual physical or emotional injury to the plaintiff
Characteristics
Action unintentional
Injury results
Action unplanned
Defences
Voluntary Assumption of Risk
To succeed; defendant must prove plaintiff clearly knew of the risk before committing their actions
Could eliminate responsibility of the defendant
Used often by drunk drivers
Defendant must prove this to be true
Inevitable accident
Harm or loss that results from situation that is unavoidable regardless or percautions
Contributory Negligence
If both plaintiff and defendant are found negligent, damages are split between them
Burden
Often used as a defence in accidents when a seatbelt is not worn