von Allison Blocka` Vor 5 Jahren
461
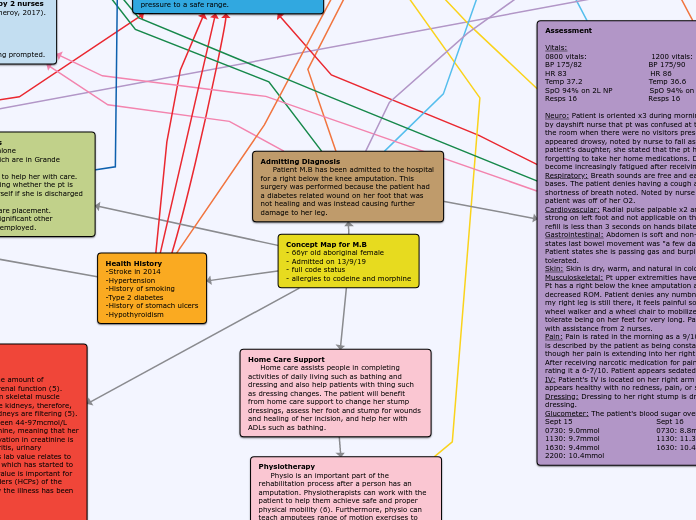
NS408 Allison Concept Map
Individuals requiring home care often need assistance with daily activities such as bathing, dressing, and wound management. For those who have undergone procedures like a below-knee amputation, specialized support becomes crucial.