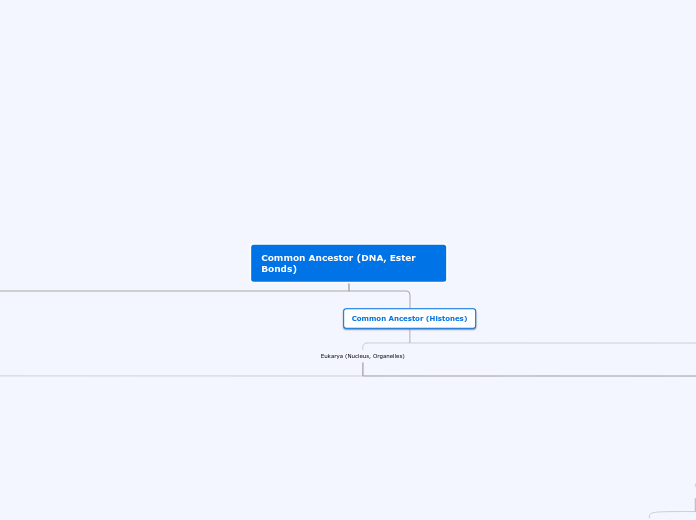
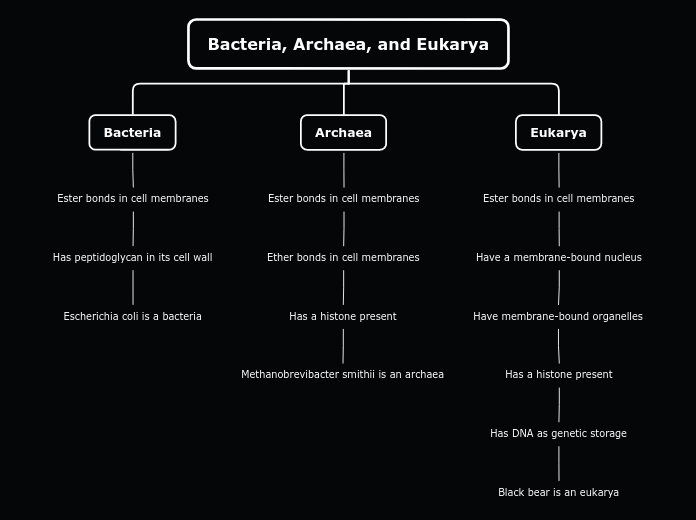
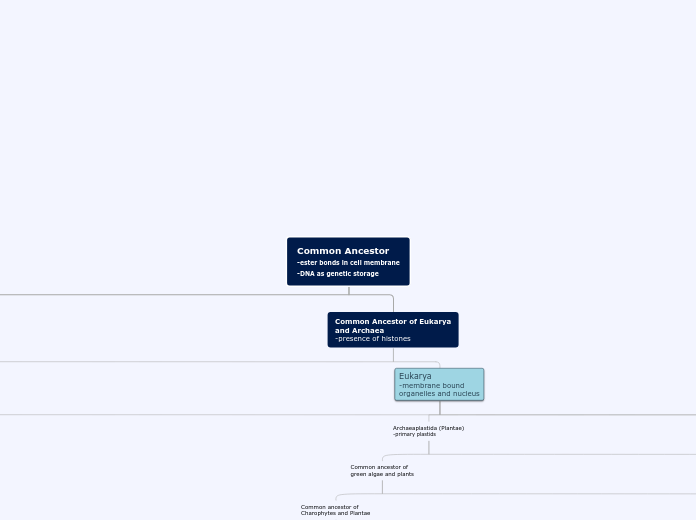
Common Ancestor (DNA, Ester Bonds)
Common Ancestor (Histones)
Archaea (Ether Bonds)
Methanobrevibacter smithii
Eukarya (Nucleus, Organelles)
Excavata ( Feeding Groove, Secondary Plastids )
euglenoids
SAR Clade
Rhizarians ( Filose Pseudopodia )
Foraminfera
Radiolarians
Alveolates ( Membraneous Vesicles, Secondary Plastids )
Dianoflagellates
Stramenopiles (Tripartite Flagellar Hair, Secondary Plastids )
Kelp
Diatoms
Unikonta (Absorptive Heterotrophy)
Amoebozoa (Pseudopodia)
Slime Molds
Opisthokonta (single posterior flagellum on swimming cells, absorptive heterotrophy )
Archaeplastida (Primary Plastids)
Glaucophyte Algae
Common Ancestor
Phycoerythrin photosynthetic pigment
Rhodophyta
Chlorophyll a & b, b-Carotene cellulose rich cell walls
Chlorophytes
Ring-Shaped cellulose-synthesizing proteins phragmoplast
Zygotic life cycle
Charophytes
Braun's stonewort (Chara braunii)
Land Plants (embryo, sporic life cycle, gametangia, sporangia, apical meristems and desiccation-resistant spores)
Liverworts
Common Liverwort (Marchantia polymorpha)
Mosses
Woolly Feather Moss (Tomentypnum nitens)
Hornworts
Field hornwort (Anthoceros agrestis)
Common Ancestor of vascular plants (xylem and phloem, leaves, dominant sporophyte, stomata and waxy cuticle, Lignin)
Common Ancestor (Megaphylls)
Seed Plants (Ovules, Pollen, Seeds, Heterospory, Wood)
Angiosperms (Flowers, Fruit, Endosperm, Ovaries)
White Water Lily (Nymphaea alba)
Southern Magnolia (Magnolia grandiflora)
Gymnosperms
Conifers
Bald Cypress (Taxodium distichum)
Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris)
Monilophytes
Horsetails
Ferns
Eastern Marsh Fern (Thelypteris palustris)
Lycophytes (Lychophylls)
Fan clubmoss (Diphasiastrum digitatum)
Bacteria (Peptidoglycan)
Escherichia coli