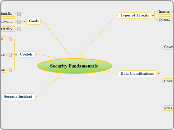
Security Fundamentals
Security Incident
Ramifications
Administrative Law
Civil Law
Criminal Law
Effective Argument
Opportunity
Means
Motive
Contols
Technical
1)Security appliances (firewalls, IPS, VPN termination)
2)Authorizations appliances (RADIUS or TACACS+ servers)
Physical
1)Security systems
2)Physical security barriers
3)Climate protection systems
4)Security personnel
Detective
Deterrent
Preventive
Administrative
1)Routine security awarness training
2)Clearly defined security policies
3)Logging config changes
4)Properly screening potential employees
Data Classifications
Roles
User
1)Accesses and uses data in accordance with an established security policy
2)Takes reasonable measures to protect the data he or she has access to
3)Uses data for only organizational purposes
Custodian
1)Keeps up to date backups
2)Verifies the intergrity of backups
3)Restores data from backups
4)Follows policy guidelines to maintain data
Owner
1)Initally determines the classification level
2)Routinely reviews documented procedures for classifying data
3)Gives the custodian the resoponsibilty of protecting the data
Charateristics
Personal Association
How personal the data is
Useful Life
How long is the data will be considered relevant
Age
How old is the data
Value
How valuable the date is to the organization
Government
Top-Secret
Reasonable probability of causing exceptionally grave damage if disclosed
Secret
Reasonalbe probability of casuing serious damage if disclosed
Confidential
Reasonaable probability of causing damage if disclosed
Sensitive but Unclassified
Could casue embarrassment but not a security threat
Unclassified
Few or no privacy requirements
Types of Threats
External
Tend to be more technical (i.e ping sweeps or port scans)
Internal
1)Have knowledge of network and available resources
2)Some level of access granted b/c of job
3)Traditional sec. mechanisms (i.e. IPS and firewalls) are ineffective against
Goals
Availability
1)Send improperly formatted data to create an unhandled exception error
2)Flood network with a denial-of-service (DoS) attack
Integrity
1)Modifying the appearance of a corporate website
2)Intercepting and altering and e-commerce transaction
3)Modifying finacial records
Confidentiality
1)Use network security mechanisms (firewalls & ACLs)
2)Require credentials (usernames & passwords)
3)Encrypt traffic