Parts of Speech
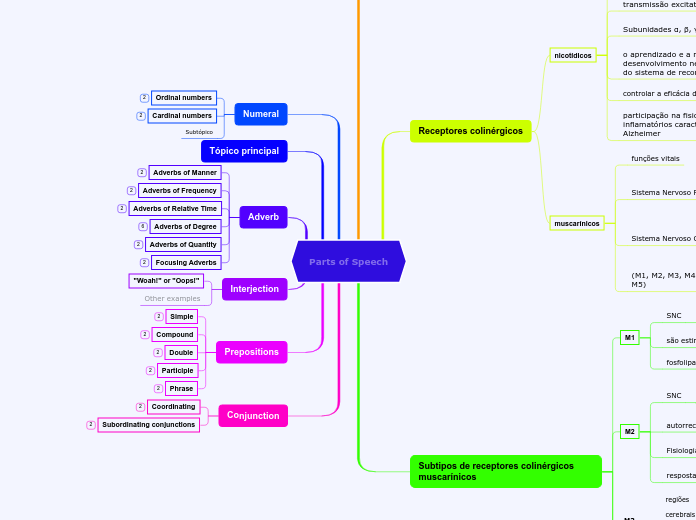
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
Conjunction
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Subordinating conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
Coordinating
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
This stew is savory and delicious.
Prepositions
A preposition is one of the most exciting parts of grammar. A preposition is used to describe the location of something in relation to something else.
Phrase
A group of words used with the force of a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
according to, by means of, owing to, with a view to, in place of, in front of, etc.
Participle
Participle preposition consists of words that end in “ing”.
regarding, barring, concerning, considering, etc.
Double
When a preposition consists of more than one word, it is called double preposition.
into, within, upto etc.
Compound
Compound preposition consists of two or more words.
on behalf of, according to, in front of, from across, etc.
Simple
When a preposition consists of one word it is called single or simple preposition.
in, at, on, to for, of, from, up, after, over, under, with, etc.
Interjection
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
Other examples
"Woah!" or "Oops!"
Adverb
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
Focusing Adverbs
Especially, Specifically, Merely, Either
Adverbs of Quantity
A lot, Little, Much
Adverbs of Degree
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
down-toners
Fairly, Rather
intensifiers
Extremely, Very
Adverbs of Relative Time
Just, Afterward, Soon, Currently
Adverbs of Frequency
Always, usually, Never
Adverbs of Manner
Carefully, Slowly
Tópico principal
Numeral
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
Subtópico
Cardinal numbers
One, two..
Ordinal numbers
First, second..
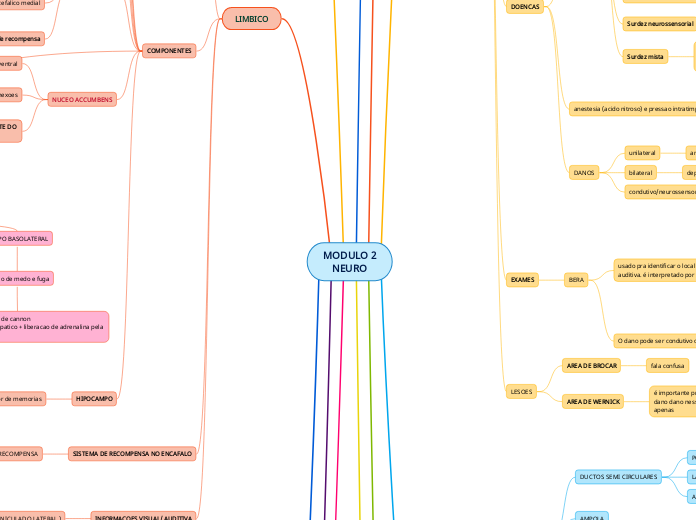
Subtipos de receptores colinérgicos muscarínicos
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
M5
sinalização intracelular iniciada pelos
receptores
RNAm
M4
vias de sinalização inibitória ou estimulatória
M1+M2
neurônios estriatais de ratos
M3
processos colinérgicos no cérebro
regiões
cerebrais
M2
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
resposta ionotrópica negativa
Fisiologia do coração
reduz a força de contração e também
a frequência de batimentos cardíacos em cobaias
autorreceptor
neurônios estriatais, no tegumento mesopontino e no núcleo motor
do nervo craniano.
M1
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
fosfolipase C24
são estimulados por carbacol
SNC
50% dos RCMs presentes no hipocampo
Receptores colinérgicos
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
muscarínicos
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
(M1, M2, M3, M4,
M5)
apenas o subtipo M5 ainda não foi totalmente caracterizado
no nível farmacológico e funcional
controle da função extrapiramidal, vestibular, em funções cognitivas como memória, aprendizado e atenção, em respostas emocionais, na modulação do estresse, no sono e na vigília
Sistema Nervoso Periférico
ações que incluem a redução da frequência e força da contração cardíaca, o relaxamento de vasos sanguíneos periféricos e a constrição das vias respiratórias (brônquios e bronquíolos).
funções vitais
nicotídicos
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
participação na fisiopatologia e nos processos inflamatórios característicos da doença de Alzheimer
controlar a eficácia da transmissão sináptica
o aprendizado e a memória, o desenvolvimento neuronal e participa
do sistema de recompensa
Subunidades α, β, γ e δ.
Cérebro e tecido muscular
Cérebro= se distribuem em pré-, pós-, peri- e extrassinápticas
atividade sináptica
neuronal
transmissão excitatória rápida
receptores ionotrópicos
Sistema Nervoso Central
Síndromes neurológicas e psiquiátricas
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Epilepsia
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
The winning athlete gets a trophy.
Transtornos de humor
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
Parkinson
Esquizofrenia
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
You look exhausted after studying all night.
Disfunção do sistema de neurotransmissão colinérgica
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
Create sentences
They have it.