Special Education Part 2
Module 1 Overview
IEP
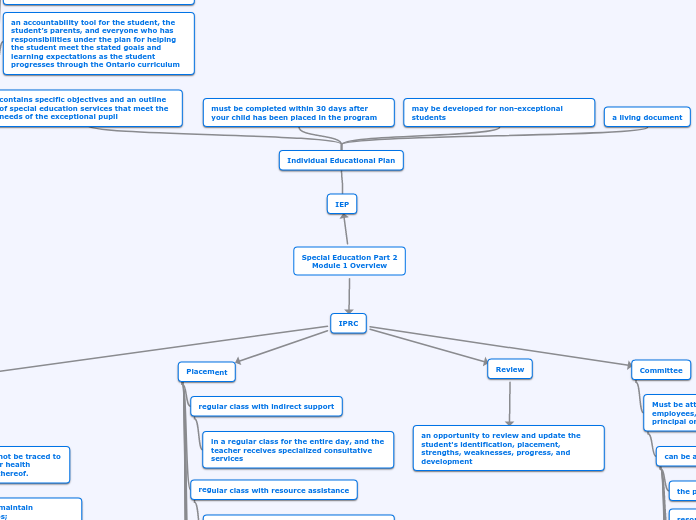
Individual Educational Plan
a living document
may be developed for non-exceptional students
must be completed within 30 days after your child has been placed in the program
contains specific objectives and an outline of special education services that meet the needs of the exceptional pupil
an accountability tool for the student, the student’s parents, and everyone who has responsibilities under the plan for helping the student meet the stated goals and learning expectations as the student progresses through the Ontario curriculum
a record of the teaching strategies specific to modified and alternative expectations and of assessment methods to be used to determine the student’s progress towards achieving these expectations
a transition plan that includes the specific goals, actions required, person(s) responsible for actions, and timelines for each educational transition where the student requires support
a statement about the methods by which your child’s progress will be reviewed
an outline of the special education program and services that will be received
a description of the student’s strengths and needs and specific educational expectations
IPRC
Committee
Must be attended by at least 3 school board employees, one of which must be a principal or supervisory officer
can be attended by:
other individuals whose presence is requested by either the parents or the principal of the student’s school
an interpreter
representative of the parents and/or of a student who is 16 years of age or older
resource people such as the student’s teacher(s), special education staff, school board support staff, or other professionals who may be needed to provide further information or clarification
the principal of the student’s school
Review
an opportunity to review and update the student's identification, placement, strengths, weaknesses, progress, and development
Placement
facility that provides the necessary care or treatment appropriate to the student’s condition
Demonstration School
residential school or students who have severe learning disabilities
Provincial School
residential school for students who are Deaf, blind, or deafblind
special education class full time
in a special education class for the entire school day.
special education class with partial integration
in a special education class for at least 50 per cent of the school day, but is integrated with a regular class for at least one instructional period daily
regular class with withdrawal assistance
in the regular class and receives instruction outside of the classroom for less than 50 per cent of the school day, from a qualified special education teacher.
regular class with resource assistance
in the regular class for most or all of the day and receives specialized instruction, individually or in a small group, within the regular classroom from a qualified special education teacher
regular class with indirect support
in a regular class for the entire day, and the teacher receives specialized consultative services
Idenification
Multiple Exceptionalities
A combination of learning or other disorders, impairments, or physical disabilities that is of such a nature as to require, for educational achievement, the services of one or more teachers holding qualifications in special education and the provision of support services appropriate for such disorders, impairments, or disabilities
Physical
Blind and Low Vision
Physical Disability
A condition of such severe physical limitation or deficiency as to require special assistance in learning situations to provide the opportunity for educational achievement equivalent to that of students without exceptionalities who are of the same age or development level
Intelluctual
Developmental Disability
a limited potential for academic learning, independent social adjustment, and economic self-support
an ability to profit from a special education program that is designed to accommodate slow intellectual development
an inability to profit from a special education program for students with mild intellectual disabilities because of slow intellectual development
Mild Intellectual Disability
learning disorder
a potential for academic learning, independent social adjustment, and economic self-support
an inability to profit educationally within a regular class because of slow intellectual development
an ability to profit educationally within a regular class with the aid of considerable curriculum modification and support services
Giftedness
An unusually advanced degree of general intellectual ability that requires differentiated learning experiences of a depth and breadth beyond those normally provided in the regular school program to satisfy the level of educational potential indicated
Communnicational
Learning Disability
One of a number of neurodevelopmental disorders that persistently and significantly has an impact on the ability to learn and use academic and other skills
is not the result of a lack of acuity in hearing and/or vision that has not been corrected; intellectual disabilities; socio-economic factors; cultural differences; lack of proficiency in the language of instruction; lack of motivation or effort; gaps in school attendance or inadequate opportunity to benefit from instruction
may be associated with difficulties in social interaction (e.g., difficulty in understanding social norms or the point of view of others); with various other conditions or disorders, diagnosed or undiagnosed; or with other exceptionalities
may typically be associated with difficulties in one or more cognitive processes, such as phonological processing; memory and attention; processing speed; perceptual-motor processing; visual-spatial processing; executive functions (e.g., self-regulation of behaviour and emotions, planning, organizing of thoughts and activities, prioritizing, decision making)
results in difficulties in the development and use of skills in one or more of the following areas: reading, writing, mathematics, and work habits and learning skills
results in (a) academic underachievement that is inconsistent with the intellectual abilities of the student (which are at least in the average range), and/or (b) academic achievement that can be maintained by the student only with extremely high levels of effort and/or with additional support
affects the ability to perceive or process verbal or non-verbal information in an effective and accurate manner in students who have assessed intellectual abilities that are at least in the average range
Speech Impairment
disorder in language formulation that may be associated with neurological, psychological, physical, or sensory factors; that involves perceptual motor aspects of transmitting oral messages; and that may be characterized by impairment in articulation, rhythm, and stress
Language Impairment
an impairment in comprehension and/or the use of verbal communication or the written or other symbol system of communication, which may be associated with neurological, psychological, physical, or sensory factors
include one or more of: language delay; dysfluency; voice and articulation development, which may or may not be organically or functionally based.
involve one or more of the form, content, and function of language in communication;
Deaf and Hard of Hearing
Autism
severe learning disorder
lack of the representational symbolic behaviour that precedes language
disturbances in: rate of educational development; ability to relate to the environment; mobility; perception, speech, and language
Behavioural
an inability to learn that cannot be traced to intellectual, sensory, or other health factors, or any combination thereof.
a tendency to compulsive reaction
excessive fears or anxieties
an inability to build or to maintain interpersonal relationships;