von Bronwyn Heard Vor 4 Jahren
389
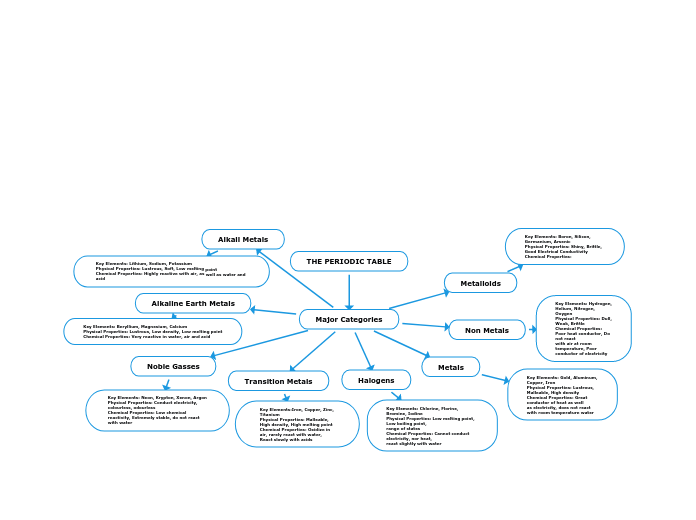
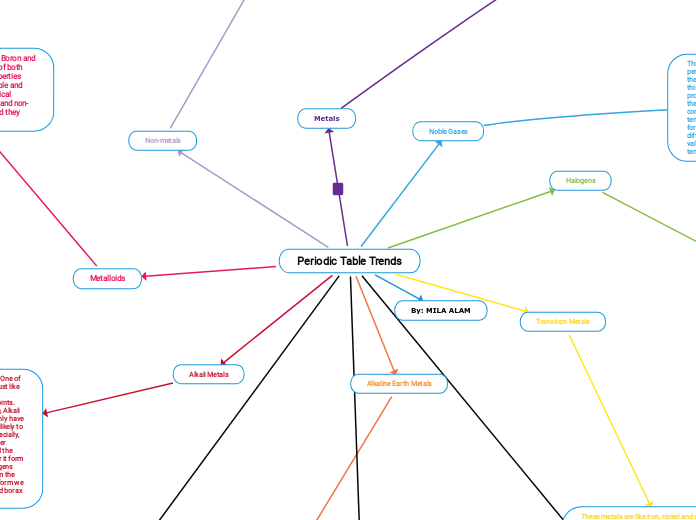
THE PERIODIC TABLE
The periodic table organizes elements into major categories based on shared physical and chemical properties. Metals, for example, are characterized by their lustrous appearance, malleability, and high density, and they are excellent conductors of heat and electricity.