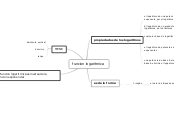
Un exponente es el valor que determina el número de veces que la base se multiplica por sí mismo. Los exponentes Representan la multiplicación repetitiva. Logaritmo de un número es el exponente al que hay que elevar la base para que nos de dicho número
Name the character
Type in the name of the character whose change throughout the story you are going to analyze.
Example: Nick Carraway.
LOGARITMOS
Character's behavior
Think of the character's behavior at the beginning of the story and look for the way it changed throughout the story.
el logaritmo de un número real positivo n, en una determinada base b, es el exponente x de b para obtener n: La base tiene que ser positiva y distinta de 1.
PROPIEDADES DE LOS LOGARITMOS
The reason for the change in behavior
What caused the character to change the first behavior you mentioned? Type in the reason for the change.
Example: 'because no one else was interested ', and he felt Gatsby shouldn't be left alone in his last moments.
Importante: el argumento de un logaritmo siempre debe ser positivo (ni negativo ni 0).
Razonamiento esencial para resolver las ecuaciones:
logb(x)=logb(y)⇒x=y
Cambio de base:
logb(x)=logc(x)logc(b)
Logaritmo de una potencia:
logb(xy)=y⋅logb(x)
Logaritmo del cociente:
logb(xy)=logb(x)−logb(y)
Logaritmo del producto:
logb(x⋅y)=logb(x)+logb(y)
propiedades:
logb(a)=c⇔bc=a
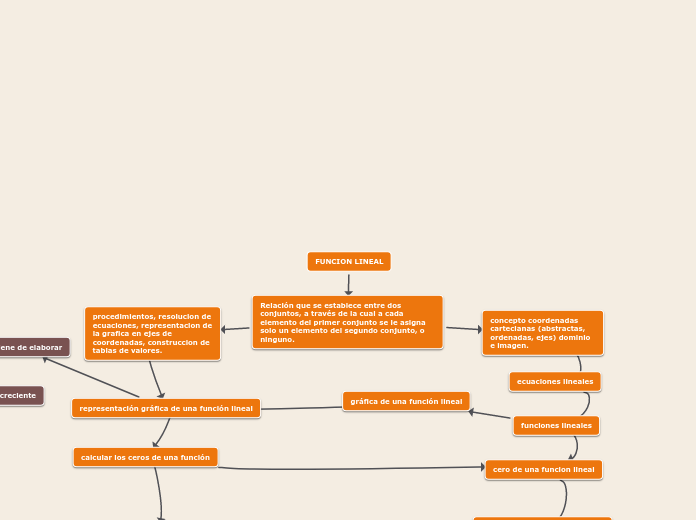
FUNCIONES EXPONENCIALES
Character's feelings
Focus on the way the character's feelings are presented at the beginning and at the end of the story, while explaining why they have changed.
Una funcion exponencial,
por lo tanto, permite aludir a
fenomenos que crecen cada vez con
mayor rapidez
PROPIEDADES GENERALES
Initial feelings
How does the character feel about a certain subject at the beginning of the story? Type in a relevant quote to support your statement.
Example: "Reserving judgements is a matter of infinite hope."
La función exponencial de una resta es igual al cociente de su aplicación al minuendo dividida por la función del sustraendo:
f (x - x?) = ax-x? = ax/ax? = f (x)/f (x?).
La función exponencial de una suma de valores es igual al producto de la aplicación de dicha función aplicada a cada valor por separado.
f (x + x?) = ax+x? = ax × ax? = f (x) × f (x?).
La función exponencial de 1 es siempre igual a la base:
f (1) = a1 = a.
La función aplicada al valor cero es siempre igual a 1:
f (0) = a0 = 1.
EXPONENTES Y LOGARITMOS
Title
Type in the title and author of the literary work that introduces the character.
Example: The Great Gatsby, by F. Scott Fitzgerald.