von A. Zimmer Vor 6 Jahren
214
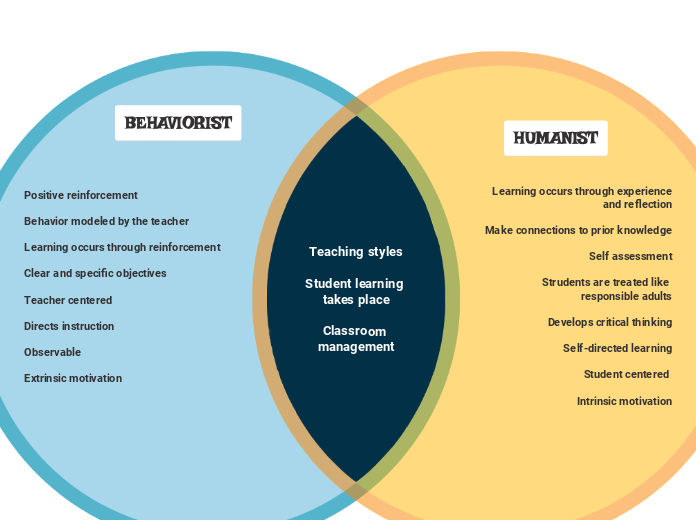
Viewpoint of Behaviourism
Behaviorism focuses on how learning occurs through the association between stimuli and responses. It posits that responses followed by reinforcement are more likely to be repeated. Learning is observed through changes in performance, which is accomplished when the learner demonstrates the correct response to a specific stimulus.