von Byck Byck Vor 3 Jahren
207
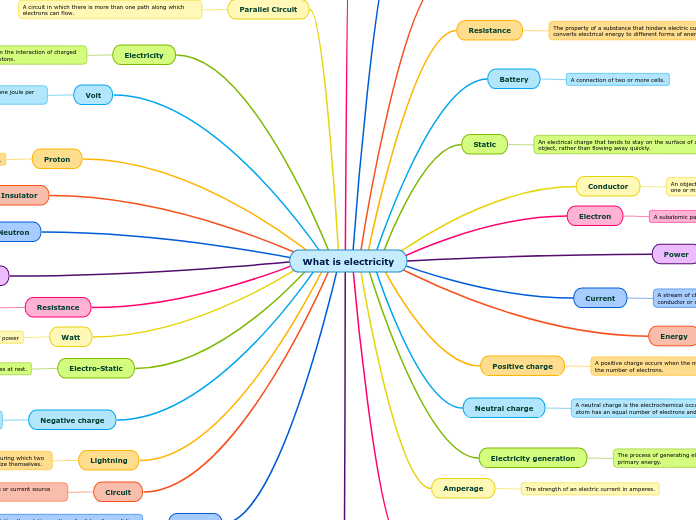
What is electricity
Electricity is a form of energy arising from the movement and interaction of charged particles like electrons and protons. It involves various concepts such as voltage, which is the potential difference or electromotive force, and resistance, which is the property of a material that opposes the flow of electric current.