por Joseph Ray hace 1 año
112
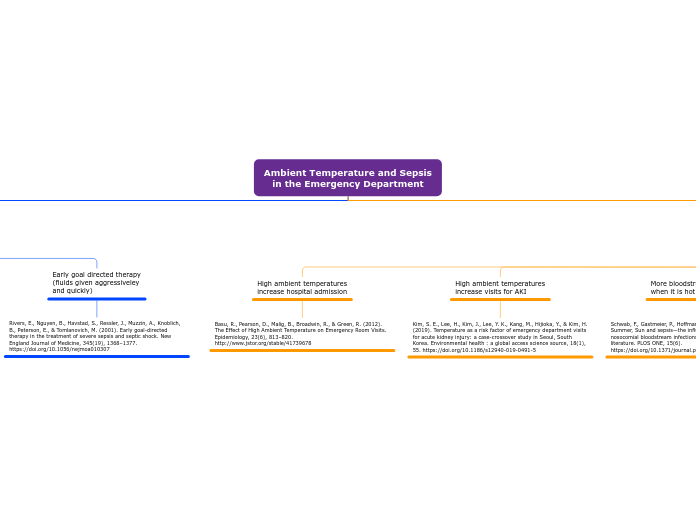
Ambient Temperature and Sepsis in the Emergency Department
Research indicates a significant correlation between high ambient temperatures and increased health issues. Notably, elevated temperatures are linked to a rise in nosocomial bloodstream infections, as well as an uptick in emergency department visits for acute kidney injury (