por Marisol Salazar hace 4 años
269
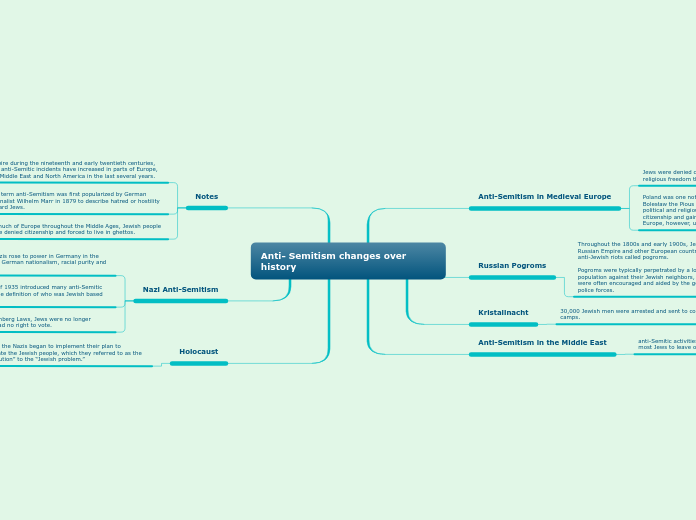
Anti- Semitism changes over history
The historical evolution of anti-Semitism demonstrates its deep-rooted and widespread impact across various regions and eras. Originating from the Middle Ages, Jewish communities faced systemic discrimination, including denial of citizenship and forced ghettoization.