por camila gomez hace 12 meses
190
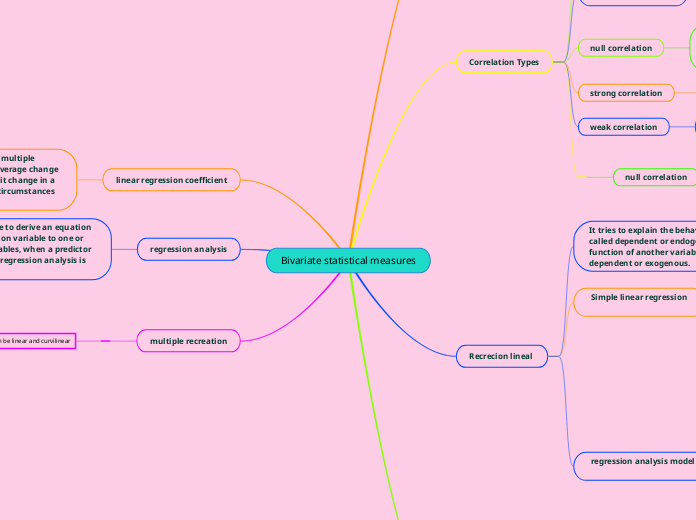
Bivariate statistical measures
The determination coefficient, also known as R square, is used to measure the degree of correlation between variables, indicating how well a model fits the data. Linear correlation assesses the stable relationship or dependence between two variables in a two-dimensional distribution.