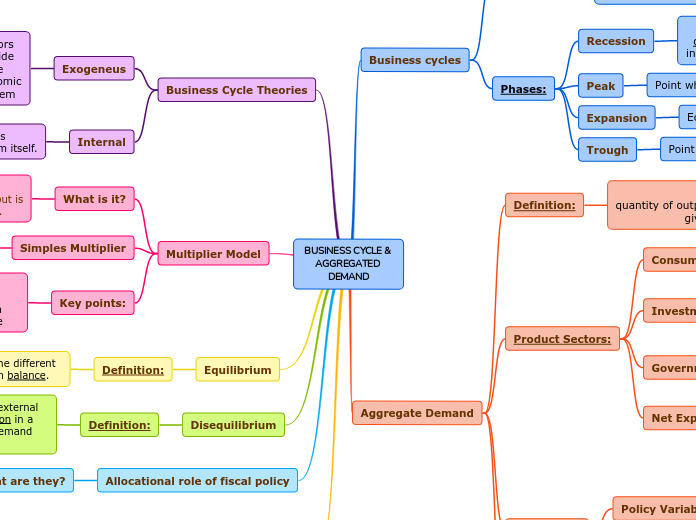
BUSINESS CYCLE & AGGREGATED DEMAND
The total expenditure curve (TE)
What it does?
Shows the level
of expenditure desired or planned by consumers and
businesses
Allocational role of fiscal policy
What are they?
Government tax and
spending programs
Disequilibrium
Disequilibrium is when external forces cause a disruption in a market's supply and demand equilibrium
Equilibrium
Is a situation where the different forces at work are in balance.
Multiplier Model
Key points:
Basic multiplier
model emphasizes the importance of shifts in AD in affecting output and income
Simples Multiplier
Equals to:
Is numerically = 1/(1 � MPC)
What is it?
Macroeconomic
theory used to explain how output is
determined in the short run.
Business Cycle Theories
Internal
Look for mechanisms
within the economic system itself.
Exogeneus
Factors outside the economic
system
EXAMPLES:
Wars, revolutions, and elections;
in oil prices, gold discoveries, and population migrations
Aggregate Demand
The AD curve slopes downward
Categories:
Exogeneous Variables:
Variables that are determined outside the AS-A framework.
Policy Variables:
Fiscal Policy
Taxes and government expenditures
Monetary policy
The central bank can affect interest rates and other financial conditions
Product Sectors:
Net Exports
(X) Which equal the value of exports minus the value of imports
Government Purchases
(G) Like tanks and school books, the services of judges and public-school teachers.
Investment
(I) Spending includes purchases of buildings, software, and equipment
Consumption
(C) Is primarily determined by disposable income
Aggregate
quantity of output that is willingly bought at a
given level of prices
Business cycles
Phases:
Trough
Point where expansion starts
Expansion
Economy is moving out of recession
Peak
Point where recessio starts
Recession
Recurring period of decline in total output,
income, and employment
Definition:
Economywide fluctuations in
total national output, income, and employment