Concept Map 2
Energy Transfer
Organism Level
Hetero and Autotrophs (Individual)
Metabolic rate how much energy an organism uses, affecting energy needs.
Energy Flow in Populations: Individual energy needs impact group energy consumption.
Energy Loss Between Levels (Community): Only about 10% of energy is passed up each trophic level; the rest is lost as heat.
Photosynthesis
Cells break down glucose with oxygen to release energy, CO₂, and water.
ATP Production: Energy from respiration is stored in ATP molecules for cellular functions
Energy Loss as Heat: Not all energy is stored; some is lost as heat during metabolic processes.
Cell Respiration
Aerobic
Requires Oxygen
Glycolosis
1st Step:
Glucose to Glucose-6-Phosphate with the enzyme hexokinase.
3rd Step:
Fructose-6-Phosphate to fructose-1-6-phosphate with the enzyme phosphofructokinase.
Output:
2 Net ATP
2 Pyruvate
2 NADH
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate Oxidation requires oxygen.
Pyruvate makes:
1 Acetyl CoA
1 NADH
Citric Acid Cycle
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle/TCA Cycle)
Step 1:
Acetyl CoA and Oxaloacetate go together and make Citrate.
Step 3:
Isocitrate becomes ketoglutarate
Output:
1 ATP
3 NADH
1 FADH2
Oxidative Phospohlation
This process is broken down into two parts, the Electron Transport Chain(ETC) and Chemiosmosis.
Chemiosmosis
Once many H+ exits into the intramitochondrial space through the ETC, ATP synthase allows H+ to go back into the matrix in through facilitated diffusion in attempt to even out on both sides. This takes ADP turning it into ATP.
Electron Transport Chain
This process includes:
Complex I
Complex II
Complex III
Complex IV
Complex Q
Cyc
NADH gives an electron to complex one turning it into NAD+. FADH2 gives electron to Complex 2, turning into FAD. They both give their electrons to Q, from Q to complex III, Complex III to Cyc, then to complex IV and given to oxygen where it makes water(H2O). Complexes I, III, and IV are proton pump which pump out H+ into the intramitochondrial space when the electrons are being passed around.
Anerobic
Doesn't Require Oxygen
Alcohol Fermentation
When there is no O2, pyruvate forms acetaldehyde and is reduced to ethanol where CO2 is released.
This reduced electrons from NADH allowing glycolysis to continue.
Lactic Fermentation
When oxygen is not present, pyruvate is reduced and forms lactate and recycled back into NAD+ allowing glycolysis to continue. In Lactic Acid fermentation CO2 is not formed.
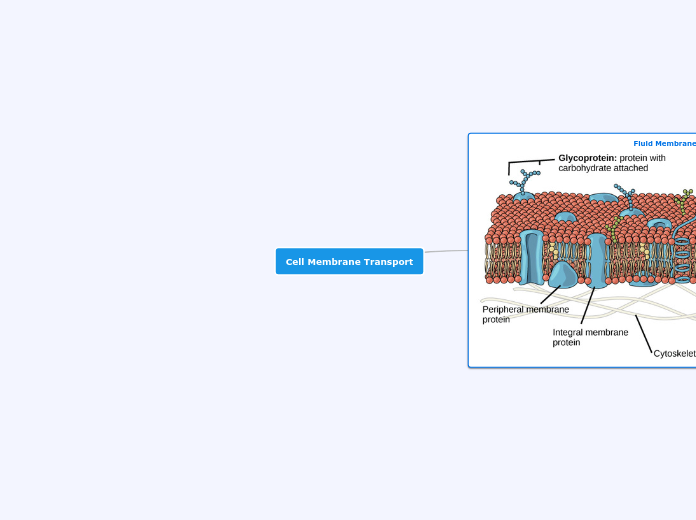
Cell Membranes
Active Transport
Contransport
Proton Pump
Electrogenic Pumps
Ion Channels
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Passive Transport
Osmosis
Subtopic
Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Cell Communications
Signalling
Local
Synaptic Signalling
Paracrine signalling
Long Distance
Hormal Signalling
Junctions
Plants
Plasmodesmata
Animals
Tight Junctions
Gap Junctions
Desmosomes