por Connor McNamara hace 12 meses
167
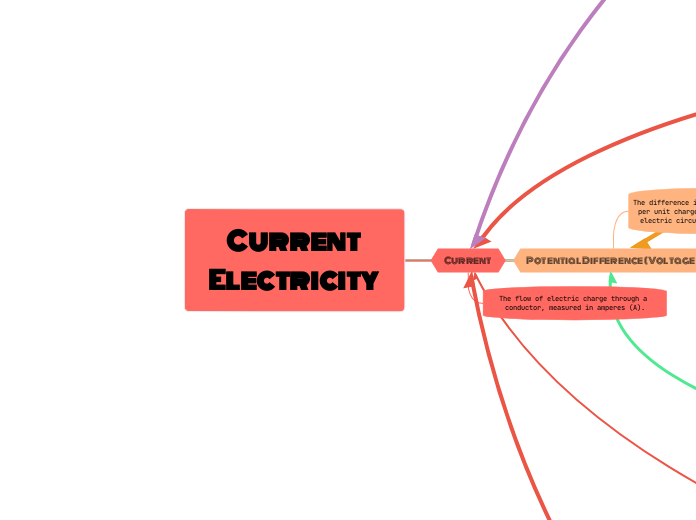
Current Electricity
An electric circuit consists of various components that work together to control the flow of electricity. A resistor is a component that resists the flow of electric current, generating heat and is measured in ohms.