Drugs of Abuse
Nicotine
Treatment for Dependence
Non-Nicotine Therapies
Selegeline
MAO inhibitor
Bupropion (Zyban)
Nortryptyline
Antidepressant
Clonidine
Alpha adrenoreceptor partial ag
Replacement Therapies
Nicotine inhaler
Nicotine nasal spray
Nicotine transdermal patch
Nicotine polacrilex (gum)
High relapse rate
Withdrawal
Psychological Dependence
Activates brain reward system
Incr. DA levels in nucleus accumbens
Incr NO production
Decr. MAO activity
Tolerance
long-lasting
develops rapidly
Peripheral vascular dz
Coronary artery dz
COPD
Chronic bronchitis
Cancer
Pharmacokinetics
t1/2 = 2hrs
eliminated by the kidney
metabolized mostly in liver, but also in lungs
rapidly absorbed and distributed
MOA
mimics Ach at cholinergic nicotinic receptors
increases the release of neurotransmitters
5HT
DA
NE
ACh
increases the release of adrenal catecholamines
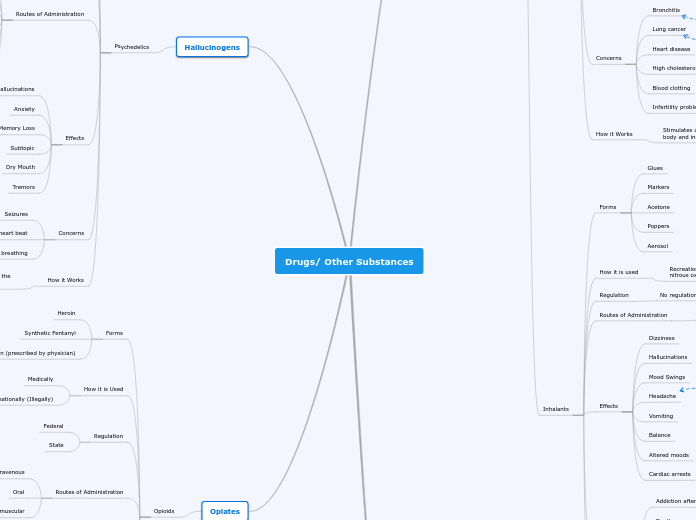
Inhalants
Organic nitrates
Amyl Nitrate
Anesthetic gases
Halothane
Nitrous oxide
found in whipped cream cannisters
Aerosols
Fluorocarbons
Industrial/Household Solvents
marker pen solvents
toluene
correction fluid
solvents in glue
degreasers
paint thinners
Opioids
(see "Opioid" map)
Hallucinogens
phenethylamine hallucinogens (NE/DA/Amphet-like)
Ecstasy (MDMA)
drug-reinforcing properties
from release of DA in brain-reward system
halucinogenic properties
from incr 5HT transmission
anesthetic hallucinogens
Phencyclidine (PCP)
dissociates individuals from themselves
long half-life (d/t enterohepatic circulation)
NMDA antag
indoleamine hallucinogens (serotonin-like)
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD)
5HT agonist
extreme tolerance develops rapidly
Marijuana
Active constituent: THC (delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol)
dronabinol (Marinol) is THC analogue
tolerance develops but disappears rapidly
"antimotivational syndrome" (controversial)
chronic lung effects (similar to nicotine)
actions:
reddening of the conjunctiva
depersonalization
relaxed, dreamlike state
increased appetite
pharmacokinetics
high lipid solubility so sequestered and slowly metabolized
can detect in drug screen days later
duration of action 2-3 hrs
onset of action almost immediate
rapidly distributed to CNS
rapidly absorbed in lungs
neuropathic pain
decrease IOP in glaucoma
appetite stimulant in AIDS
prevent n/v during chemo
MOA: unknown
has something to do with CB1 receptors and G proteins
Stimulants
increase DA, NE, 5HT avalability in the synapse
AE:
Post spree crash, withdrawal
sexual d/f
tachycardia and HTN
dangerous, bizzare behavior
anxiety, insomnia
extraordinary tolerance can develop
Acute Actions
increased motor activity
decreased appetite
elevated mood
euphoria
Amphetamine analogues
Phenteramine (Adipex-P)
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
Methamphetamine (Desoxyn)
long t1/2
Amphetamine (Dexedrine)
ADHD
Narcolepsy
Modafinil is another choice for narcolepsy tx
it has less likelyhood of adiction than amphet.'s
toxicity
see also "Cocaine: Toxicity"
necrotizing arteritis
inhibits MAO (so NE builds up)
increases release of DA
short t1/2
Cocaine
more rapidly absorbed and distributed
metabolized by plasma and liver cholinesterase
toxicity:
Toxic psychosis
Coronary vasospasm, Arrythmia, MI
Cerebrovascular hemorrhage
Seizures
"Crack Baby"
b/c cocaine decreases uterine bloodflow, thus causing fetal hypoxia
perferation of nasal septum
indications:
topical anesthesia
metab to benzoylecgonine and ecgonine methlyester
blocks DA transporters/reuptake sites
Sedative-Hypnotics
aka CNS Depressants
act at GABA-A receptor complex
Incr duration of Cl channel opening
Barbituates
much more risk for abuse than BZ's!!
long acting
Phenobarbital
contraindications:
acute intermittent porphyria
phenobarbital induces delta-ALA synthase, which increases porphyrin biosynthesis
uses:
neonatal jaundice
congenital hyperbilirubinemia
withdrawal syndrome from sed/hyp's
duration of action influenced by pH of urine
25% excreted unchanged
short-intermediate acting
Pentobarbital
less lipid soluble
regional anesthesia
preanesthetic
ultrashort acting
Thiopental
rapid redistribution to less vascular tissues
general anesthesia
highly lipid soluble
Incr frequency of Cl channel opening
Benzodiazepines
Short-Med. duration
Chloridiazepoxide
Incr Cl conductance
Alcohols
Methanol
metabolized by ADH to formaldehyde, then oxidized to formic acid (toxic)
Tx
Ethanol administration
Poisoning
Seizures, coma
Acidosis
Blindness
Ethanol
MOA: acts w/ specific site on GABA-A Receptor to facilitate opening of Cl channels (by incr conductance) which leads to hyperpolarization and inhibition of neuronal activity
also allosterically inhibits activity of excitatory glutamate receptors (NMDA subtype)
Indications: Antiseptic, solvent for other Rx
Drug therapy
reduces craving
Acamprosate
competitive inhib of NMDA Glutamate receptor
Naltrexone
reduces craving and prevents relapse
opioid recptor antag
causes you to feel bad symptoms earlier
Disulfram
causes "acetaldehyde syndrome"
confusion
hypotension
sweating
HA
flushing
chelates the cofactors necessary for acetaldehyde DH
Drug interactions
phentoin and warfarin
Chronic EtOH
induces liver microsomal enzymes
incr metab
Acute EtOH
inhibs liver microsomal enzymes
decr metab
aspirin, other NSAIDS
GI bleeding
other sedatives (BZ, Antidepress., Antihistam.)
Contraindications
seizure d/o
pregnancy
liver disease
ulcers
Actions
Chronic
FAS
cancer
cardiomyopathy
precipitates DM
pancreatitis
cirrhosis
incr NADH/NAD ratio
thiamine deficiency
Korsakoff's syndrome
Wernicke's encephalopathy
peripheral neuropathy
Acute
n/v
Diuresis
inh ADH release
CNS
high dose
more severe CNS depression (coma, death)
moderate dose
neuronal inhibition (CNS depression)
low dose
neuronal disinhibition (behavioral stimulation)
vasodilation and decr HR