edua
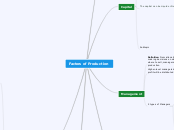
Meeting individual and business needs
Empowerment
Staff make their own decisions about work planning
Job enrichment
Group of employees complete a whole stage of production and take responsibility for quality
Job enlargement
Giving staff extra tasks or responsibilities
Job rotation
Staff exchange jobs of comparable skill around the organisation
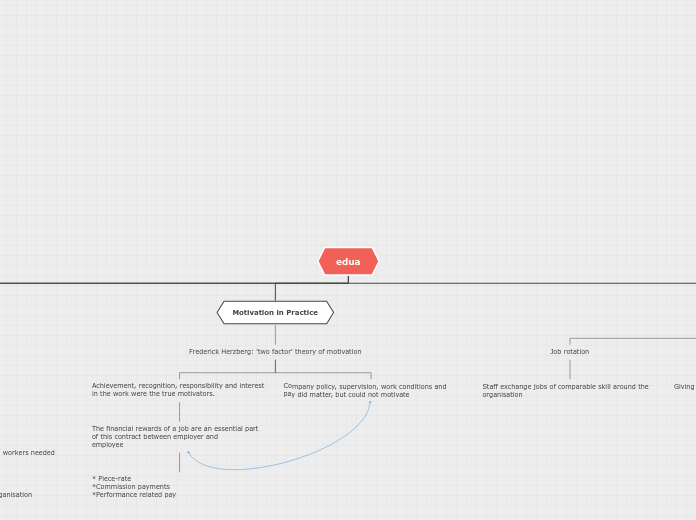
Motivation in Practice
Frederick Herzberg: 'two factor' theory of motivation
Company policy, supervision, work conditions and pay did matter, but could not motivate
Achievement, recognition, responsibility and interest in the work were the true motivators.
The financial rewards of a job are an essential part of this contract between employer and
employee
* Piece-rate *Commission payments *Performance related pay
Motivation and business growth
In 1943 the US psychologist, Abraham Maslow proposed that people are motivated by a
'hierarchy of needs'
In 1960 Douglas McGregor described two distinctive styles of management: Theory X and
Theory Y.
. In Theory X managers believed workers needed discipline
The NDA Way shows how the organisation demonstrates its values.
Theory Y saw self-motivated employees with complex
needs and a natural urge to be creative.
The value of motivation
Motivation refers to the energy and commitment with which an individual or group
performs a task or role. It affects almost every aspect of business.
Motivated workers make a more favourable impact on customers and other stakeholders
An unmotivated workforce
could have a negative impact on the business through:
• lower productivity
• more accidents
• higher rates of absenteeism
• more conflict
• less readiness to learn or change
• more need for supervision.