por Elsa Murray hace 5 años
290
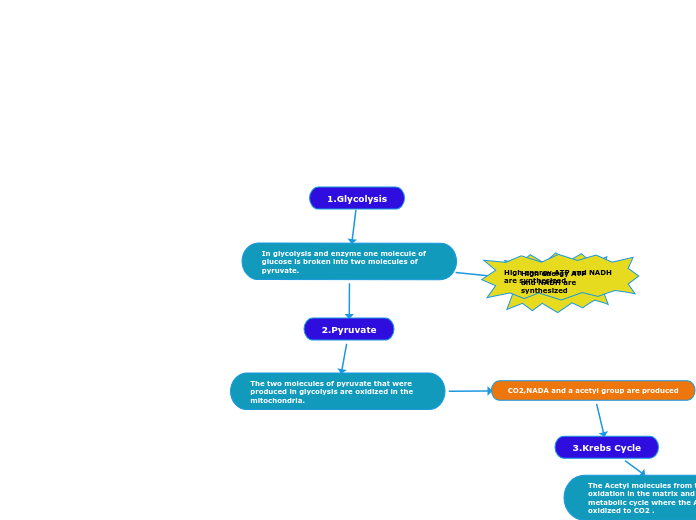
Energy systems
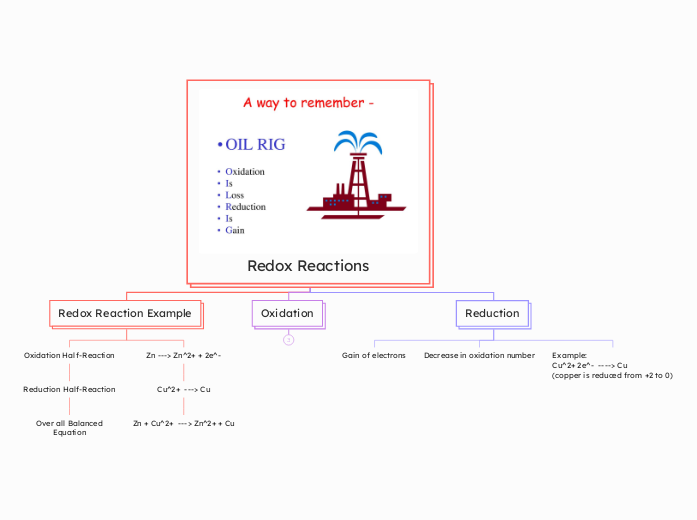
The text discusses various biochemical processes, focusing on their mechanisms and distinctions. Oxidation and reduction are defined by electron transfer, with oxidation involving the loss of electrons and reduction the gain.