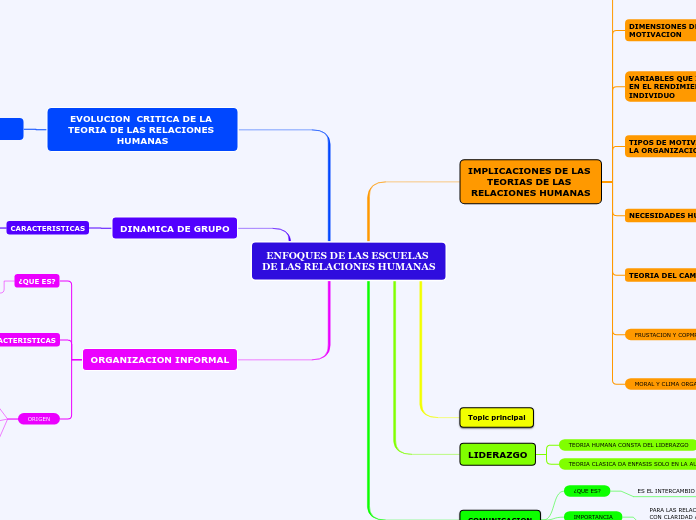
ENFOQUES DE LAS ESCUELAS
DE LAS RELACIONES HUMANAS
Conflict is present everywhere in the world around us. We experience conflict on a daily basis, and it can be minor or major.
Conflict in a story is a struggle between opposing forces. Characters must act to confront those forces and there is where conflict is born. If there is nothing to overcome, there is no story. Conflict in a story creates and drives the plot forward.
ORGANIZACION INFORMAL
In this type of conflict, a character must take on society itself, and not a single person. The character stands at odds with societal norms and realizes the necessity to work against these norms. This is an external conflict.
ORIGEN
LA MOVILIDAD DEL PERSONAL EN LA EMPRESA ALTERA LA COMPOSICION DE LOS GRUPOS SOCIALES
LA INTERACION PROVOCADA POR LA ORGANIZACION FORMAL
LOS INTERESES COMUNES
Give examples of man versus society conflict in the real world.
ESTANDARES DE DESEMPEÑO EN LOS GRUPOS INFORMALES
COLABORACION ESPONTANEA
ESTATUS:LAS PERSONAS INTERACTUAN
RELACION DE COHESION O DE ANTAGONISMO
Give examples of man versus society conflict in a literary work.
CONJUNTO DE ITNERACCIONES Y RELACIONES ESPONTANEOS QUE SE ESTABLECENM ENTRE LAS PERSONAS COMO ORGANIZACION INFORMAL
DINAMICA DE GRUPO
This situation results from a protagonist working against what has been foretold for that person. While this conflict was more prevalent in stories where gods could control fate, such as in ancient Greek dramas, there are still examples of this type of conflict in more contemporary literature.
CARACTERISTICAS
Give examples of man versus fate conflict in a literary work.
COHESION INTERNA
ESTRUCTURA DINAMICA DE COMUNICACIONES
SINALIDAD, ES DECIR UN OBJETIVO COMUN
EVOLUCION CRITICA DE LA TEORIA DE LAS RELACIONES HUMANAS
A more contemporary type of conflict, this situation results from humans involved in a struggle with man-made machines. This is an external conflict.
CRITICAS CONTRA LA TEORIA DE LAS RELACIONES CLASICAS
Give examples of man versus machine conflict in a literary work.
ENFOQUE MANIPULADOR DE LAS RELACIONES HUMANAS
PARCIALIDAD EN LAS CONLUSIONES
LIMITACION DLE CAMPO EXPERIMENTAL
CONCEPCION INGENUA Y ROMANTICA DEL OBREO
PERCEPCION INCORRECTA DE LOS PROBLEMAS DE LAS RELACIONES HUMANAS
OPOSICION CERRADA A LA TEORIA CLASICA
COMUNICACION
REDES
EXISTEN VARIAS OPCIONES DE REDES QUE ENVIEN UN MENSAJE
IMPORTANCIA
PARA LAS RELACIONES INTERPERSONALES Y EXPLICA
CON CLARIDAD A LOS SUBTEMAS LAS RAZONES
DE LAS DECISIONES QUE TOMAN
¿QUE ES?
ES EL INTERCAMBIO DE INFORMACION ENTRE LAS PERSONAS
LIDERAZGO
This conflict develops from a protagonist’s inner struggles and may depend on a character trying to decide between good and evil or overcoming self-doubt. This conflict has both internal and external aspects, as obstacles outside the protagonist's force them to deal with inner issues.
TEORIA CLASICA DA ENFASIS SOLO EN LA AUTORIDAD
TEORIA HUMANA CONSTA DEL LIDERAZGO
Topic principal
IMPLICACIONES DE LAS
TEORIAS DE LAS
RELACIONES HUMANAS
A situation in which two characters have opposing desires or interests. The typical scenario is a conflict between the protagonist and antagonist. This is an external conflict.
MORAL Y CLIMA ORGANIZACIONAL
ES U IMPULSO PARA HACER UN ESFUERZO
PARA ALCANZAR LOS OBJETIVOS ORGANIZACIONAL Y AHI NACE EL CONPTO MORAL
FRUSTACION Y COPMPESACION PROVOCA
ALINEACION Y APATIA
AGRESIVIDAD
ALTERACION Y OTROS COMPORTAMIENTOS
TEORIA DEL CAMPO DE LEWIS
Give examples of man versus self conflict in the real world.
ESTOS FUNCIONAN COMO UN CAMPO DINAMICO
SE BASA EN EL COMPORTAMIENTO HUMANO SE DERIVA DE HECHOS CONSISTENTES
NECESIDADES HUMANAS BASICAS
Give examples of man versus self conflict in a literary work.
NECESIDADES DE AUTORELACION
NECESIDADES FISIOLOGICAS
NECESIDADES PSICOLOGICAS
TIPOS DE MOTIVACION EN
LA ORGANIZACION
Give examples of man versus nature conflict in the real world.
MOTIVACION TRANSCENDENTE
IMPORTA EL SISTEMA DE
LOS INCENTIVOS
MOTIVACION EXTRINSECA
ASPECTO OBJETIVO
MOTIVACION INTRISECA
ASPECTO SUBJETIVO
VARIABLES QUE INTERVIENE
EN EL RENDIMIENTO DEL
INDIVIDUO
Give examples of man versus nature conflict in a literary work.
CONDICIONES LAORALES
CONDICIONES PERSONALES
DIMENSIONES DE LA
MOTIVACION
Give examples of man versus man conflict in the real world.
RESPONSABILIDADES
RECONOCIMIENTO
RELACIONES PERSONALES
INFLUENCIA DE LA
MOTIVACION HUMANA
Give examples of man versus man conflict in a literary work.
HOMO ECONOMICO, EL COMPORTAMIENTO DEL HOMBRE ES MOTIVADO POR EL DINERO O RECOMPENSA