por THALIA OTERO hace 5 años
875
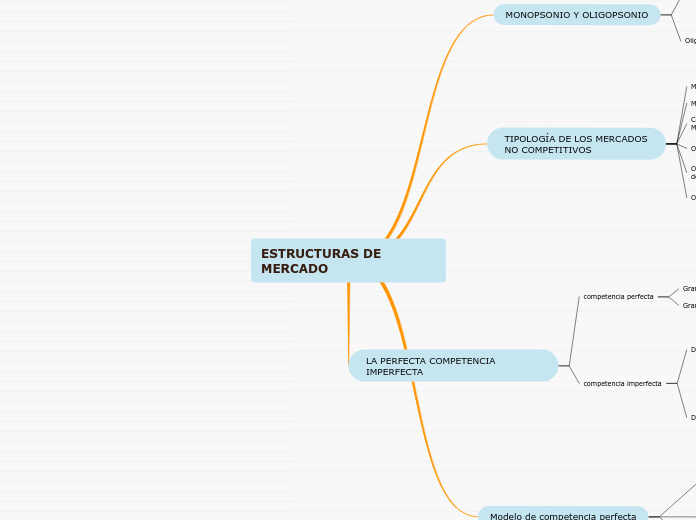
ESTRUCTURAS DE MERCADO
La estructura de los mercados se divide en competencia perfecta e imperfecta. En la competencia perfecta, hay muchos productores y consumidores, lo que equilibra el precio de mercado.
por THALIA OTERO hace 5 años
875

Ver más
Use this template to test your knowledge on some of Medieval Europe's most important events. Write down the names of important figures who have marked history.
Who is the Italian artist who painted the top of the Sistine Chapel?
This artist is also the creator of the famous sculpture statue of David.
Type in the answer.
Who was the Italian artist who painted Mona Lisa?
He became world famous for also being a prolific scientist, inventor, engineer, mathematician, and writer.
Type in the answer.
Who was the English physicist who created the laws of motion that govern all objects, including the force of gravity?
Type in the answer.
What scientist claimed that the Earth revolved around the Sun?
He was also put on trial by the Catholic Church for publishing a book with this theory. Type in the answer.
Who was the famous Italian writer who advised rulers that “the ends always justify the means”?
Type in the answer.
Who was the English writer who became famous for his plays and sonnets about love, fantasy, betrayal, politics, government, and ancient Rome?
Debido a lo anterior, el precio de equilibrio es menor al que obtendría la oferta en condiciones de competencia perfecta
Se compra en el mercado una cantidad menor a la demanda efectiva de la sociedad
Debido a lo anterior el oferente vende a un precio mayor al que existiría en la competencia perfecta
Se abastece el mercado con una cantidad menor a aquella que las fuerzas productivas pueden fabrica