Factorizacion
Diferencia de cuadrados perfectos
Factorizacion de cubos
Suma o diferencia de cubos de perfectos
Cubo perfecto de Binomio
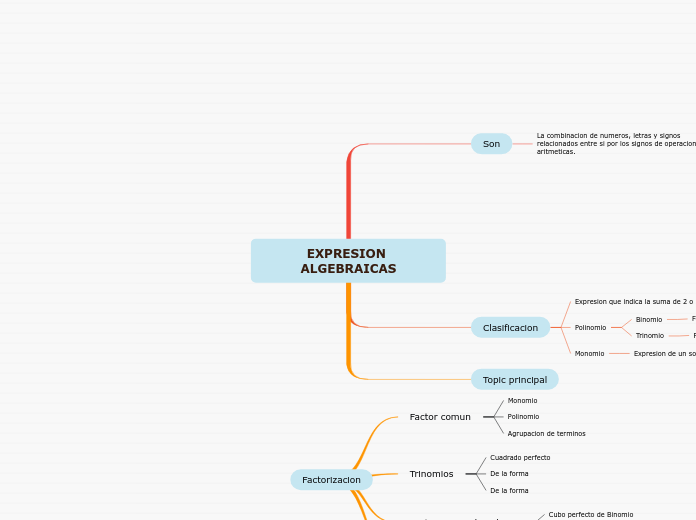
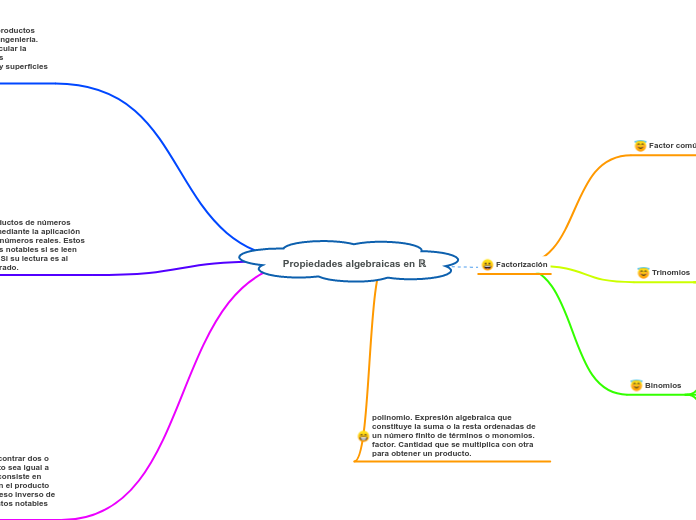
Trinomios
De la forma
Cuadrado perfecto
Factor comun
Agrupacion de terminos
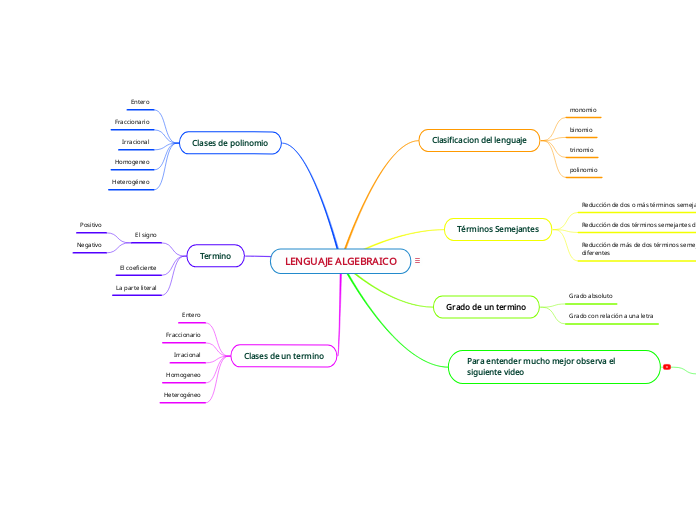
Orden de un polinomio
Ordenar terminos con respecto a los exponentes de una literal
De forma
Descendente
Ascendente
Grado del polinomio
Absoluto
Mayor grado absoluto de cada termino
Relativo
Mayor exponente que tiene la letra en el polinomio
REDUCCION DE TERMINOS SEMEJANTES
Signos de agrupacion 1.Parentesis 2.Corchetes 3.Llaves
Con difrente signo se resta al mayor coeficiente el menor y se pone el signo de .
Con el mismos signo se suman coeficientes y se pone ese mismo signos
EXPRESION ALGEBRAICAS
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
Topic principal
Clasificacion
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
Monomio
Expresion de un solo termino
Polinomio
Your character(s) need(s) motivation in order to solve the challenge(s).
Trinomio
Secondary characters might also have motives that lead them to cross paths with the main character or which might trigger them to help the main character.
Formado por 3 terminos
Binomio
Why does your character need to confront this challenge? What does he/she expect to accomplish by solving it?
See a few examples:
- will marry in 3 days
- can fix the mistakes of the past
Formado por 2 terminos
Expresion que indica la suma de 2 o mas terminos
Each story has a main character and that character usually needs to solve a problem or challenge. The character's challenge is the one that creates tension throughout the story.
Pueden ser semejantes o no
Type in any other challenges which other characters in the story need to face.
Son
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
La combinacion de numeros, letras y signos relacionados entre si por los signos de operaciones aritmeticas.
Characters are essential to a good story. Usually, the protagonist(s) is/are the most affected by the plot. Introduce a character by focusing on their actions, interests, and occupation, as the physical appearance doesn't make a difference in most cases.
Termino algebraico
Type in the name of your character.
Elementos
Add other qualities/attributes of the character.
Literal
Letras que aparecen en el termino
Exponente
Numero de veces que se utiliza un numero como factor para multiplicarse por si mismo
Coeficiente
Signo
Este nos indica si el termino es positivo o negativo
Grado de un polinomio
Choose the type of your chacter:
Protagonist (main character)Antagonist (main character's opponent)Flat (stereotypical character)Round (his/ her personality develops throughout the story)Static (doesn't evolve as a person throughout the story)Dynamic (dramatical change in personality)Confidant (the main character trusts him/ her)Foil (contrasting character who enhances the personality of another character)Other
Exponente de cada literal
Grado relativo
Grado absoluto
Suma de los exponentes de sus literales