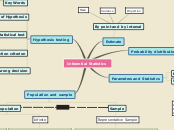
Inferential Statistics
Population and sample
Sample
Representative Sample
Part of a population that retains the characteristics of this
Population
Infinite
Population is too big and It is impossible or unaffordable to measure all individuals
Finite
Population is small and It is possible to measure all individuals
Hypothesis testing
Risk of a wrong decision
Error Type II
Error Type I
Rejection criterion
Bilateral (Two Tail Test)
Unilateral (One Tail Test)
Statistical test
Acceptance region
Rejection region
Kind of Hypothesis
Ha : Alternative hypothesis
H0 : Null hypothesis
Key Words
Paired population
Equal variances
Compare Processes
Parameters and Statistics
Statistics
Actions or functions of the sample data that help characterize the distribution of such data
Parameters
Representative and descriptive value of a population as ...
σ : Standard deviation
μ: Mean
Probability distributions
Distribution
derived from sampling
Chi-square distribution
Student's t-distribution
Distribution F
used in quality control
binomial distribution
geometric distribution
hypergeometric distribution
Poisson
Estimate
By point and by interval
Variance
Mean
Proportion